Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Hepatol. Nov 18, 2016; 8(32): 1370-1383
Published online Nov 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i32.1370
Published online Nov 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i32.1370
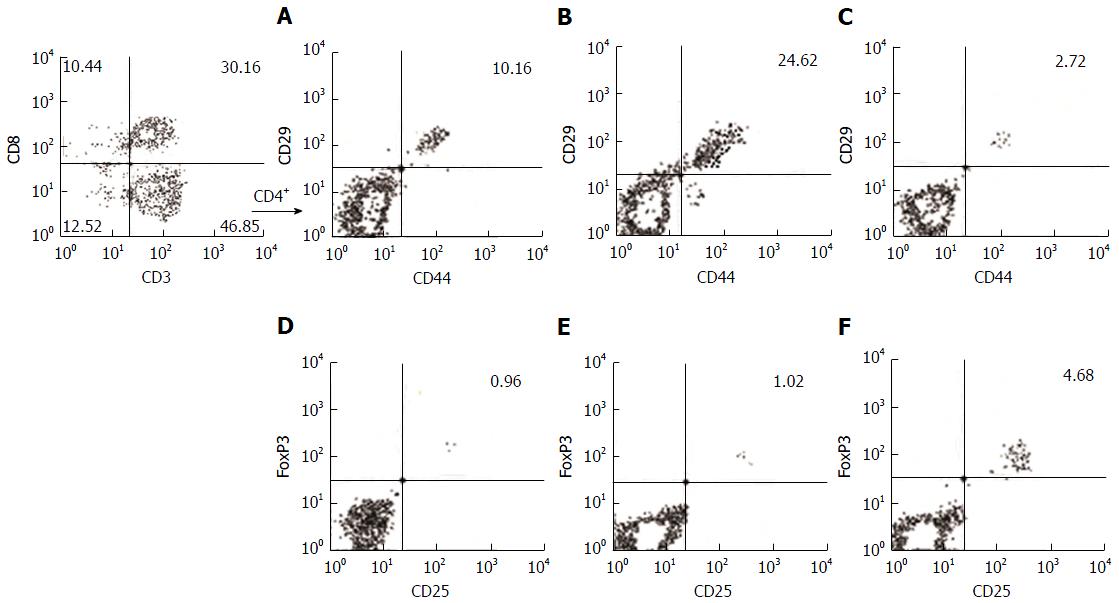
Figure 2 Hepatitis A virus Ag-activated CD4+ T cells in acute liver disease caused by hepatitis A virus.
The data from three subjects selected from our study groups were used to represent the gating strategy to select CD29+CD44+ and CD25+FoxP3+ on CD4+ cells (CD3+CD8-). Representative contour plots of the frequency of migratory T helper cells (%) in HAV Ag-activated mononuclear cells from healthy subjects (A), patients with acute hepatitis A (B), patients with acute liver failure with HAV infection (C) and in HAV Ag-activated regulatory T cells from healthy subjects (D), patients with acute hepatitis (E), and patients with acute liver failure (F). HAV: Hepatitis A virus.
- Citation: Melgaço JG, Soriani FM, Sucupira PHF, Pinheiro LA, Vieira YR, de Oliveira JM, Lewis-Ximenez LL, Araújo CCV, Pacheco-Moreira LF, Menezes GB, Cruz OG, Vitral CL, Pinto MA. Changes in cellular proliferation and plasma products are associated with liver failure. World J Hepatol 2016; 8(32): 1370-1383
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i32/1370.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i32.1370