Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Hepatol. Jan 28, 2016; 8(3): 162-182
Published online Jan 28, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i3.162
Published online Jan 28, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i3.162
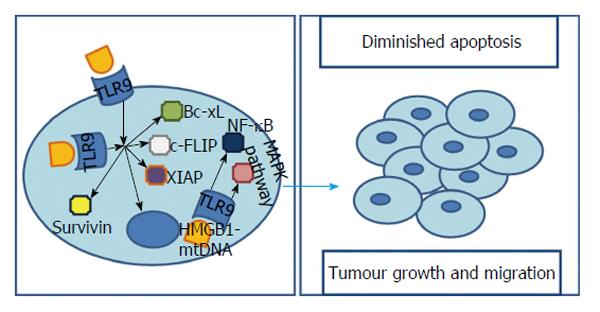
Figure 5 Toll-like receptor 9’s signalling pathways influencing hepatocarcinoma.
TLR9 is present not only in the cytoplasm but also on cells’ membrane. However, it is still controversial whether cytoplasmatic stimulation results in increased cell viability. Independently, membrane receptors’ stimulation results, not only, in up-regulation of apoptosis inhibitors such as survivin, Bcl-xL, XIAP and c-FLIP, but also, in a modulation of oncogenic genes with a major contribution in tumorigenesis and cancer progression. Additionally, a cytoplasmatic HMGB1-mtDNA interaction was proved to be capable of activating TLR9 and MAPK pathway as well as NF-κB leading to augmented survival, growth, proliferation, differentiation and migration of cancer cells. TLR9: Toll-like receptor 9; XIAP: X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein; c-FLIP: Cellular FLICE-Like inhibitory protein; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-κB: Nuclear transcription factor kappa B; HMGB1: High mobility group box 1.
- Citation: Lopes JAG, Borges-Canha M, Pimentel-Nunes P. Innate immunity and hepatocarcinoma: Can toll-like receptors open the door to oncogenesis? World J Hepatol 2016; 8(3): 162-182
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i3/162.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i3.162