Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Hepatol. Jan 28, 2016; 8(3): 162-182
Published online Jan 28, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i3.162
Published online Jan 28, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i3.162
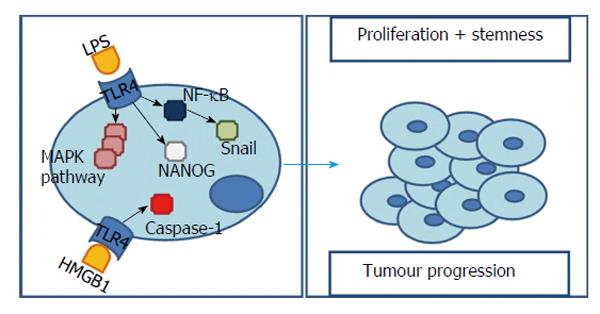
Figure 4 Toll-like receptor 4’s signalling pathways influencing hepatocarcinogenesis.
Bacterial LPS is capable of initiate TLR4 signalling and subsequently activate NF-κB and MAPK signalling pathways. In one hand, in a HCC cell line incubated with bacterial LPS both TLR4 expression and MAPK signalling pathways are significantly augmented, contributing to cell survival and proliferation. On the other hand, TLR4 over-expression contributes to an EMT through MAPKs pathway and Snail. Additionally, NANOG induces TICs’ formation. Both are considered to be the molecular basis of tumour cell infiltration and metastasis. HMGB1’s stimulation of TLR4 with caspase-1 activation is related with maturation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and consequent tumorigenesis and tumour progression. TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; LPS: Lipopolysaccharides; HCC: Hepatocarcinoma; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; TICs: Tumour-initiating stem-like cells; NF-κB: Nuclear transcription factor kappa B; HMGB1: High mobility group box 1.
- Citation: Lopes JAG, Borges-Canha M, Pimentel-Nunes P. Innate immunity and hepatocarcinoma: Can toll-like receptors open the door to oncogenesis? World J Hepatol 2016; 8(3): 162-182
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i3/162.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i3.162