Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Hepatol. Oct 18, 2016; 8(29): 1244-1250
Published online Oct 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i29.1244
Published online Oct 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i29.1244
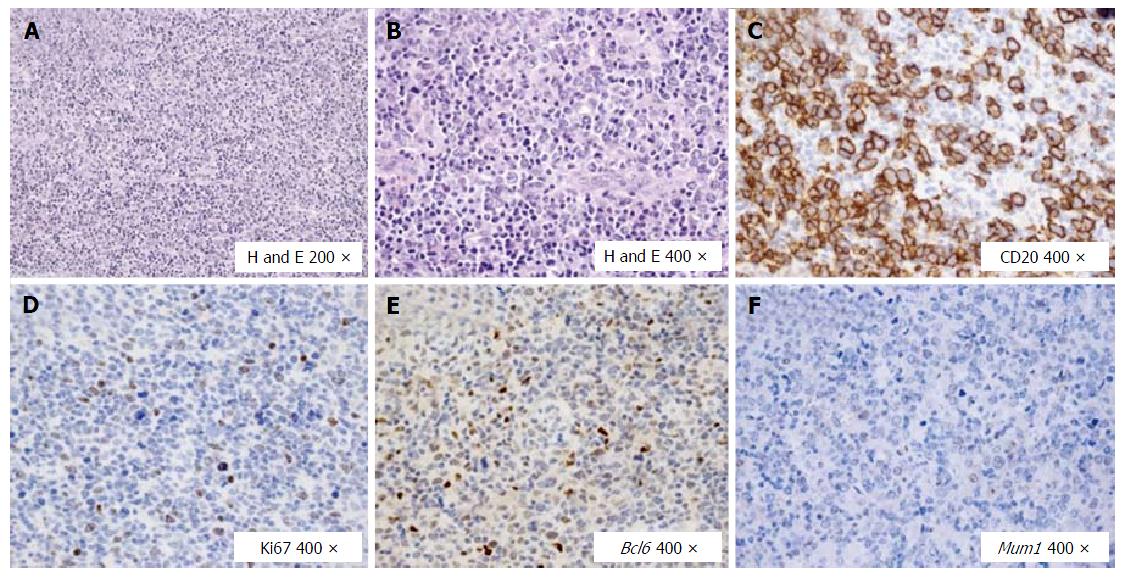
Figure 1 Histological and immunohistochemical features of the diffuse large B cell lymphoma at the primary diagnosis.
A: In the lymph node a polymorphic lymphoid population is seen; B: Large lymphoid cells prevailed; C: These large cells were B CD20+; D: The proliferation rate marked by Ki67 was around 20% with respect to the overall population, but about 40% if compared with the blastic B cell population; E: The large B cells expressed mainly the germinal center marker Bcl6; F: Mum1 was not found expressed at the primary diagnosis. DLBCL: Diffuse large B cell lymphoma; H and E: Hematoxylin and eosin; CD: Clusters of differentiation; Ki67: Cellular marker for proliferation; Bcl6: B cell lymphoma 6; Mum1: Multiple myeloma oncogene 1.
- Citation: Galati G, Rampa L, Vespasiani-Gentilucci U, Marino M, Pisani F, Cota C, Guidi A, Picardi A. Hepatitis C and double-hit B cell lymphoma successfully treated by antiviral therapy. World J Hepatol 2016; 8(29): 1244-1250
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i29/1244.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i29.1244