Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Hepatol. Aug 18, 2016; 8(23): 976-984
Published online Aug 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i23.976
Published online Aug 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i23.976
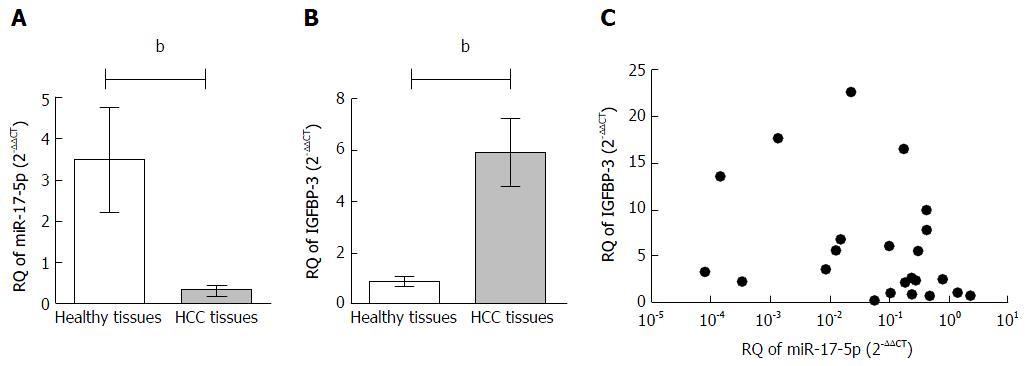
Figure 1 Expression profile of microRNA-17-5p and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 and their correlation in liver tissues.
The expression of miR-17-5p and IGFBP-3 were investigated in 10 healthy and 23 HCC liver tissues using TaqMan qRT-PCR and normalized in each sample to RNU6B endogenous control for miR-17-5p and B2M for IGFBP-3. A: miR-17-5p expression was down-regulated in non-metastatic HCC patients compared to healthy liver tissues (P = 0.0012); B: Regarding IGFBP-3, its mRNA expression showed a significant higher expression in HCC tissues compared to healthy tissues (P = 0.0041). Statistical analysis was performed using the Mann-Whitney test; C: Relative quantitation (RQ) values of miR-17-5p and IGFBP-3 mRNA in HCC tissues were analyzed using Pearson’s method of correlation. A non-significant inverse correlation was found with Pearson’s r = -0.3244 (P = 0.1310). bP < 0.01. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; IGFBP-3: Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3; miR-17-5p: MicroRNA-17-5p; qRT-PCR: Real-time quantitative PCR.
- Citation: Habashy DA, El Tayebi HM, Fawzy IO, Hosny KA, Esmat G, Abdelaziz AI. Interplay between microRNA-17-5p, insulin-like growth factor-II through binding protein-3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol 2016; 8(23): 976-984
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i23/976.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i23.976