Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Hepatol. Jul 28, 2016; 8(21): 902-914
Published online Jul 28, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i21.902
Published online Jul 28, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i21.902
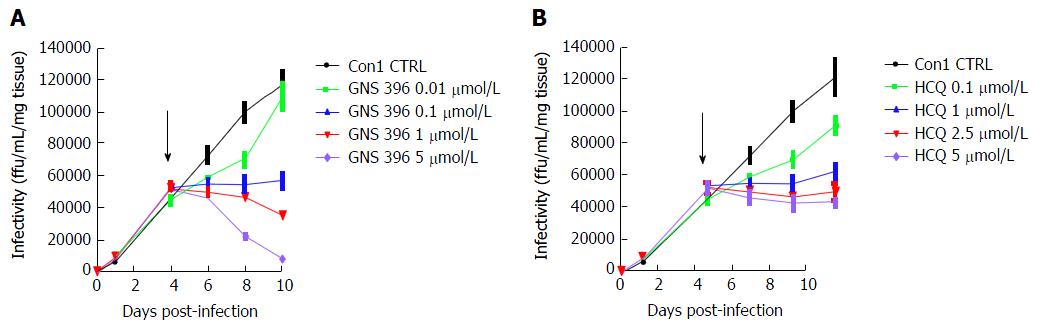
Figure 7 Dose-dependent inhibition of primary-culture-derived virus infectivity in primary adult human cell culture–grown hepatitis C virus Con1 infected liver slices by treatment either with GNS-396 (A) or hydroxychloroquine (B).
Kinetics of infectivity of culture supernatants from human liver slices infected by HCV Con1 (MOI = 0.1) and treated either GNS-396 (A) or with HCQ (B) or at day 4 post-infection for 6 d. A: Con1 (black line), P < 0.0001; GNS-396 0.01 μmol/L (green line), P < 0.0003; GNS-396 0.1 μmol/L (blue line), P < 0.019; GNS-396 1 μmol/L (red line), P < 0.05; GNS-396 5 μmol/L (purple line), P < 0.05; B: Con1 (black line), P < 0.0001; HCQ 0.1 μmol/L (red line), P < 0.0001; HCQ 1 μmol/L (green line), P < 0.0001; HCQ 2.5 μmol/L (red line), P < 0.0001; HCQ 5 μmol/L (purple line), P < 0.0003. Each curve represented the average of 2 independent infections performed in triplicate from 2 different donors. Values are expressed as means ± SE. The results were compared using the two-paired student’s test. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; HCQ: Hydroxychloroquine; MOI: Multiplicity of infection; CTRL: Control-treated liver slices.
- Citation: Lagaye S, Brun S, Gaston J, Shen H, Stranska R, Camus C, Dubray C, Rousseau G, Massault PP, Courcambeck J, Bassisi F, Halfon P, Pol S. Anti-hepatitis C virus potency of a new autophagy inhibitor using human liver slices model. World J Hepatol 2016; 8(21): 902-914
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i21/902.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i21.902