Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Hepatol. Jul 28, 2016; 8(21): 902-914
Published online Jul 28, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i21.902
Published online Jul 28, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i21.902
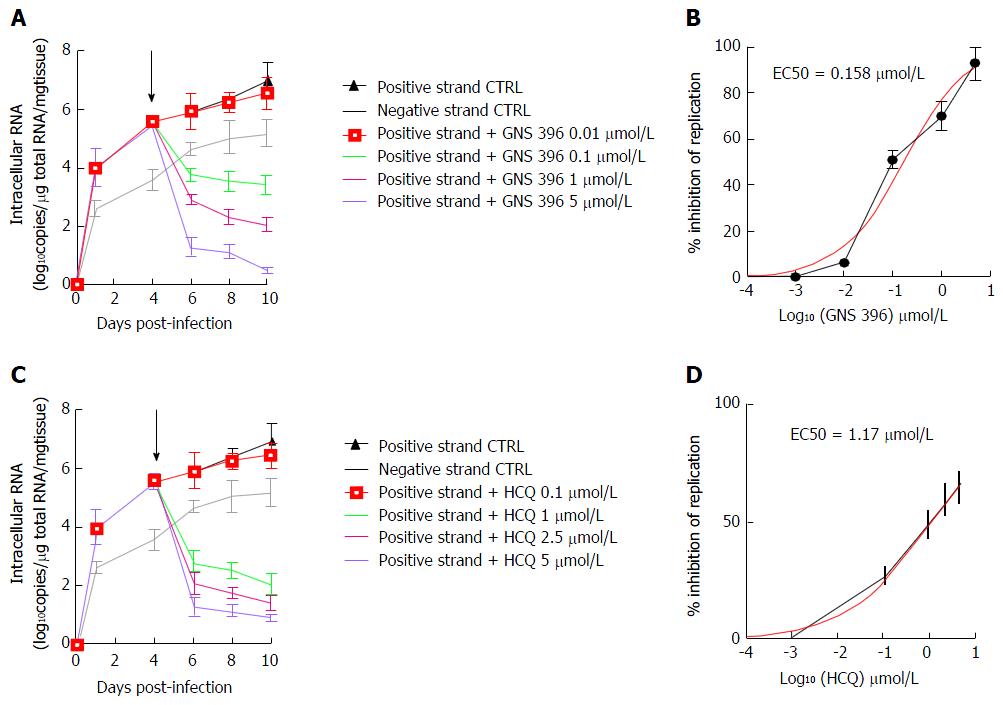
Figure 6 Inhibition of hepatitis C virus RNA replication by treatment either with GNS-396 or hydroxychloroquine in a dose-dependent manner in primary adult human cell culture-grown hepatitis C virus Con1 infected liver slices.
Human liver slices were infected overnight with HCVcc Con1 (MOI = 0.1). The supernatant is then removed, the human liver slices washed and cultured. The liver slices and culture supernatants were collected different times post-infection. At day 4 post-infection, the liver slices were treated with increasing concentrations either of GNS-396 (0.01, 0.1, 1, 5 μmol/L) (A, B) or HCQ (C, D) for 6 d (black arrow: Start of the treatment either with GNS-396 or HCQ). Human HCVcc Con1 infected liver slices were lysed to evaluate intracellular levels of positive- and negative-strand HCV RNA by specific strand RT-qPCR at 1, 4, 6, 8, 10 d post-infection. The results were compared using the two-paired Student’s test. Values are expressed as means ± standard errors: (A) HCV RNA replication by treatment with GNS-396: Positive strand (black line), P < 0.03; negative strand (grey line), P < 0.013, GNS-396 0.01 μmol/L (red line), P < 0.04; GNS-396 0.1 μmol/L (green line), P < 0.05; GNS-396 1 μmol/L (pink line), P < 0.05; GNS-396 5 μmol/L (blue line), P < 0.05; (C) HCV RNA replication by treatment with HCQ: Positive strand (black line), P < 0.03; negative strand (grey line), P < 0.015; HCQ 0.1 µmol/L (red line), P < 0.0001; HCQ 1 μmol/L (green line), P < 0.0001; HCQ 2.5 μmol/L (pink line), P < 0.01; HCQ 5 μmol/L (blue line), P < 0.03. The detection of negative strand of HCV RNA evidences active replication as well as the increase overtime of both positive and negative strands of HCV RNA; B: Inhibition of HCV replication (%) with GNS-396 treatment P < 0.0038; D: Inhibition of HCV replication (%) with HCQ treatment P < 0.0013. The replication was significantly inhibited in a dose-dependent manner in presence of increasing concentrations either of GNS-396 (B) or HCQ (D) for 6 d. HCVcc: Cell culture-grown hepatitis C virus; HCQ: Hydroxychloroquine; qRT-PCR: Quantitative technique consisting of reverse transcription followed by real-time polymerase chain reaction; MOI: Multiplicity of infection; CTRL: Control-treated liver slices.
- Citation: Lagaye S, Brun S, Gaston J, Shen H, Stranska R, Camus C, Dubray C, Rousseau G, Massault PP, Courcambeck J, Bassisi F, Halfon P, Pol S. Anti-hepatitis C virus potency of a new autophagy inhibitor using human liver slices model. World J Hepatol 2016; 8(21): 902-914
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i21/902.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i21.902