Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Hepatol. Jul 28, 2016; 8(21): 902-914
Published online Jul 28, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i21.902
Published online Jul 28, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i21.902
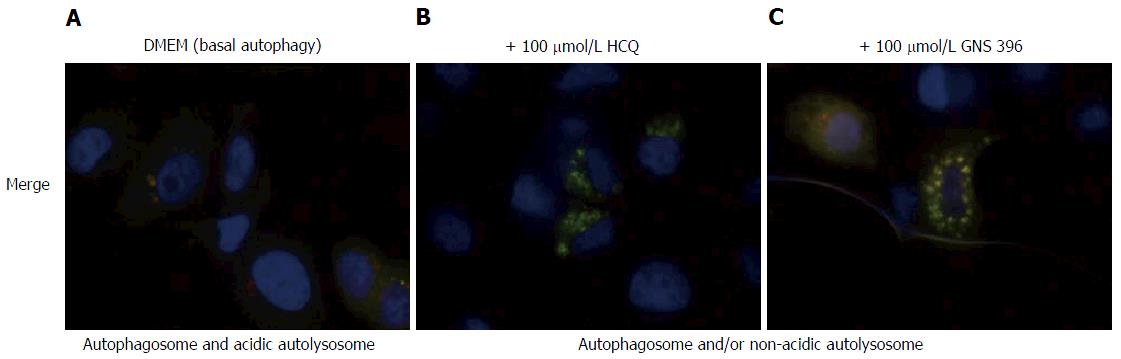
Figure 4 Inhibition of autophagic flux by treatment with GNS-396 in SkBr3 mRFP-EGFP-LC3 stable cell line.
Autophagic flux was monitored using the mRFP-EGFP-LC3 tandem-tagged fluorescent protein in SkBr3 mRFP-EGFP-LC3 stable cell line. A: SkBr3 mRFP-EGFP-LC3 stable cell line without any treatment is representative of basal autophagy; SkBr3 mRFP1-EGFP-LC3 stable cell line was treated either with (B) 100 μmol/L HCQ or (C) 100 μmol/L GNS-396 during 6 h. In green/red merged images, yellow punctua (i.e., mRFP+EGFP+) indicate autophagosomes or non-acidic autolysosomes, while red punctua (i.e., mRFP+EGFP) indicate autolysosomes. HCQ is used as a positive control of autophagy inhibition. HCQ: Hydroxychloroquine; DMEM: Dulbecco’s modified eagles’s medium; LC3: Microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain.
- Citation: Lagaye S, Brun S, Gaston J, Shen H, Stranska R, Camus C, Dubray C, Rousseau G, Massault PP, Courcambeck J, Bassisi F, Halfon P, Pol S. Anti-hepatitis C virus potency of a new autophagy inhibitor using human liver slices model. World J Hepatol 2016; 8(21): 902-914
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i21/902.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i21.902