Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Hepatol. Jul 8, 2016; 8(19): 815-824
Published online Jul 8, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i19.815
Published online Jul 8, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i19.815
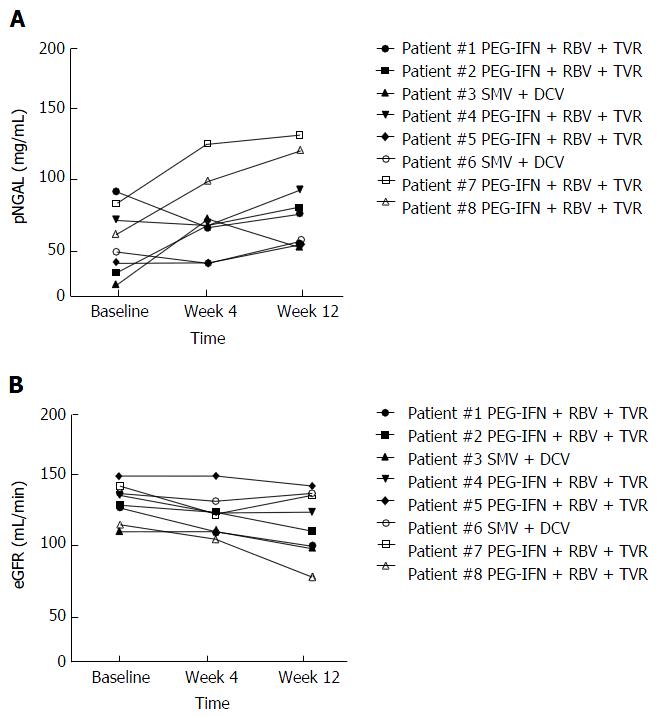
Figure 4 Evolution of neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (A) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (B) in 8 patients during the first 12 week of hepatitis C virus therapy with directly acting antiviral containing regimens.
Number of patients and respective treatment for hepatitis C virus infection are specified. PEG-IFN: Pegylated-interferon; RBV: Ribavirin; TVR: Telaprevir, SMV: Simeprevir; DCV: Daclatasvir; eGFR: Estimated glomerular filtration rate; NGAL: Neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin.
- Citation: Strazzulla A, Coppolino G, Di Fatta C, Giancotti F, D’Onofrio G, Postorino MC, Mazzitelli M, Mammone SV, Gentile I, Rivoli L, Palella E, Gravina T, Costa C, Pisani V, De Maria V, Barreca GS, Marascio N, Focà A, Fuiano G, Gulletta E, Torti C. Is neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin useful in hepatitis C virus infection? World J Hepatol 2016; 8(19): 815-824
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i19/815.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i19.815