Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Hepatol. Jul 8, 2016; 8(19): 796-814
Published online Jul 8, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i19.796
Published online Jul 8, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i19.796
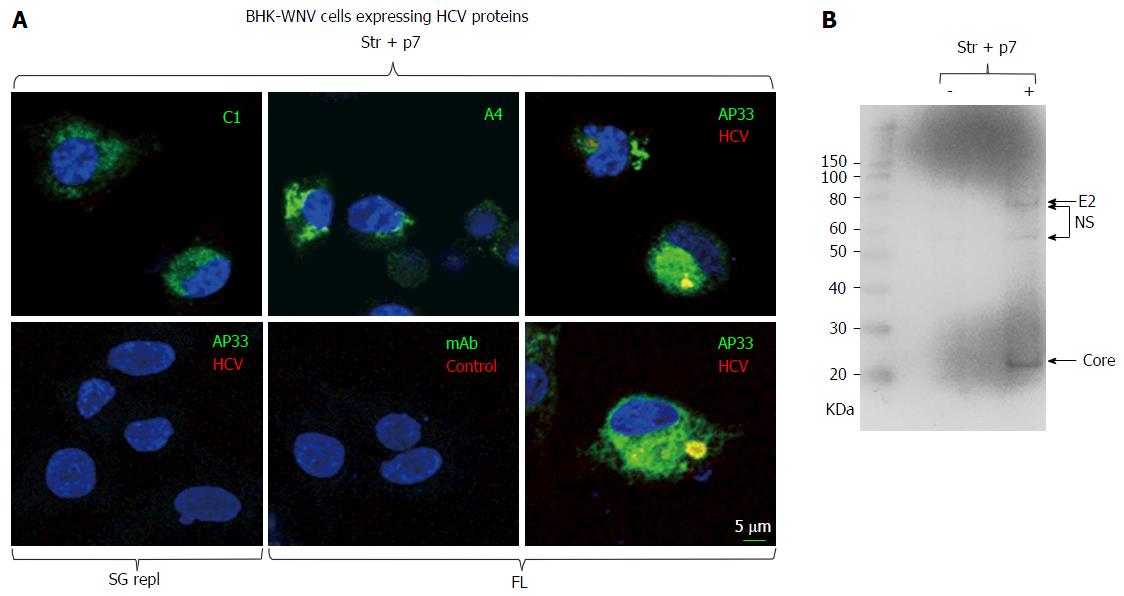
Figure 1 Immunodetection of hepatitis C virus proteins of genotype 1a expressed in baby hamster kidney-West Nile virus cells.
A: A plasmid encoding Str + p7 of HCV strain H77 (genotype 1a) from an early human cytomegalovirus promoter or a system of plasmids (P2B) expressing a subgenomic replicon or genome (FL) of same genotype in the cytoplasm (8) were transfected in BHK-WNV cells; after 2 d, IF study was performed with monoclonal antibodies (green) targeting core 9-21 (C1), envelope E1 (A4) and E2 (AP33) (28) glycoproteins of strain H77 (all IgG1a), or anti-rabbit IgG mouse Ab (mAb) of same isotype; and with human serum IgG (red) obtained from a patient recently cured from an infection of same genotype (HCV) or uninfected (control). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue) and cells were observed with a laser-scanning confocal microscope; B: BHK-WNV cells were either mock transfected (-) or transfected with a system of plasmids expressing the genome of H77 strain (+); after 3 d, cell lysates were prepared and human anti-HCV IgG tested in (a) were used as a Western blot probe. The scale on the left shows molecular weight markers. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; BHK-WNV: Baby hamster kidney-West Nile virus; Str + p7: Structural and p7 genes.
- Citation: Triyatni M, Berger EA, Saunier B. Assembly and release of infectious hepatitis C virus involving unusual organization of the secretory pathway. World J Hepatol 2016; 8(19): 796-814
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i19/796.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i19.796