Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Hepatol. Apr 28, 2015; 7(6): 874-884
Published online Apr 28, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i6.874
Published online Apr 28, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i6.874
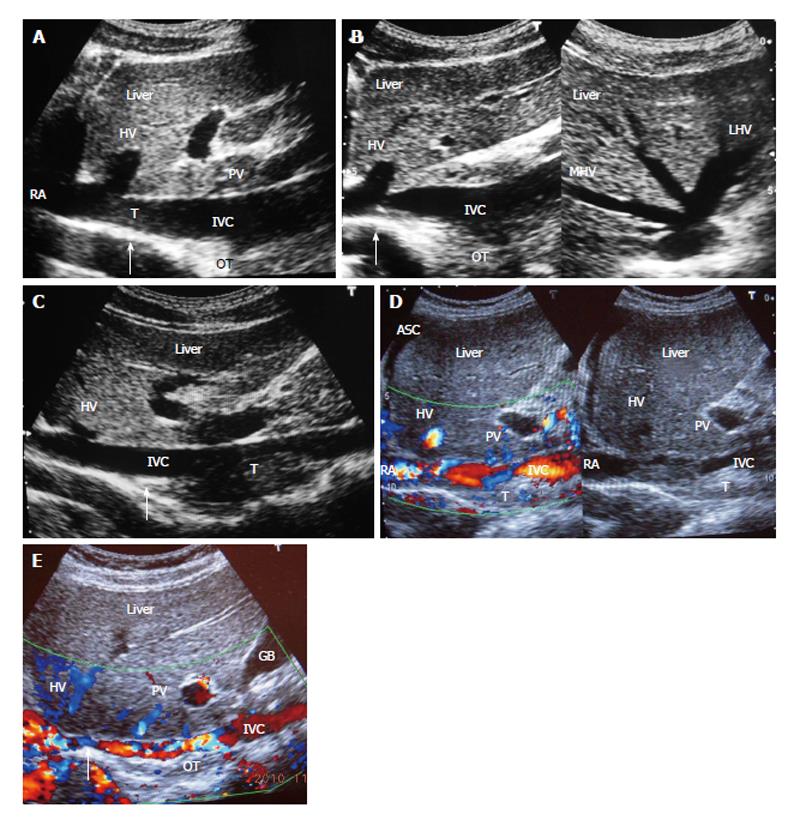
Figure 2 Ultrasonography showing thrombi of different ages in inferior vena cava due to recurrent acute exacerbations.
A: Ultrasonography showing mild stenosis of inferior vena cava (IVC) with thick echoic posterior wall at cavo-atrial junction. It shows recent thrombus (T) and old organized thrombus (OT) deposited during recurrent acute exacerbation (AE); B: Ultrasonography showing stenosis of IVC at cavo-atrial junction, with OT along posterior wall just distal to it. Middle hepatic vein (MHV) and left hepatic vein (LHV) hepatic veins are patent; C: Ultrasonography showing mild stenosis of IVC at cavo-atrial junction and thrombus of different ages along the posterior wall of the IVC; D: Ultrasonography showing features of HV outflow obstruction-hepatomegaly and ascites (ASC) in a patient with IVC stenosis near cavo-atrial junction and IVC filled with recent and old organized T; E: Ultrasonographic evidence of recurrent AE; Color Doppler ultrasonography showing layers of linear old OT along posterior wall of the hepatic portion of the IVC narrowing its lumen. Arrow indicates to the site of initial lesion in IVC. USG also shows segmental stenosis of HV. PV: Portal vein; HV: Hepatic vein; RA: Right atrium; GB: Gall bladder.
- Citation: Shrestha SM. Liver cirrhosis in hepatic vena cava syndrome (or membranous obstruction of inferior vena cava). World J Hepatol 2015; 7(6): 874-884
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v7/i6/874.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i6.874