Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Hepatol. Apr 28, 2015; 7(6): 859-873
Published online Apr 28, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i6.859
Published online Apr 28, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i6.859
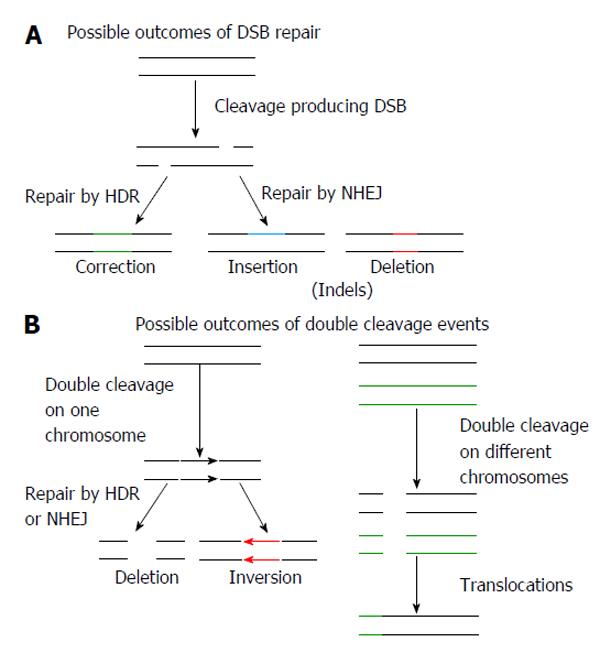
Figure 5 Potential effects of using genome editing endonucleases.
A: Nuclease induced double strand breaks (DSB) may be repaired by homology directed repair (HDR), resulting in corrections that may be to a single base pair or thousands of base pairs. Repair by non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) may result in non-specific insertions and deletions (indels); B: The introduction of two nucleases targeting the same chromosome may result in large deletions or inversions of the DNA. Chromosomal translocations may occur when two DSBs are introduced on different chromosomes.
- Citation: Nicholson SA, Moyo B, Arbuthnot PB. Progress and prospects of engineered sequence-specific DNA modulating technologies for the management of liver diseases. World J Hepatol 2015; 7(6): 859-873
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v7/i6/859.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i6.859