Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Hepatol. Apr 18, 2015; 7(5): 777-786
Published online Apr 18, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i5.777
Published online Apr 18, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i5.777
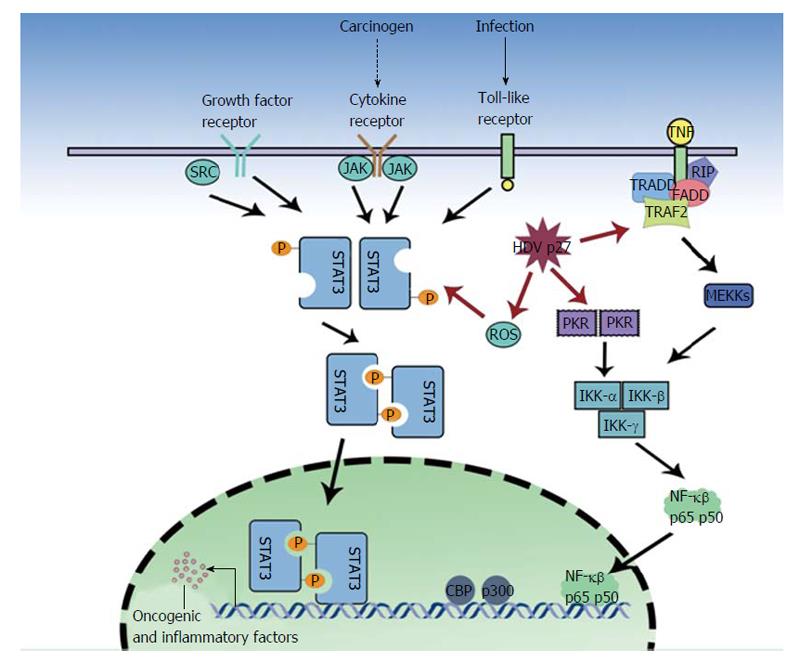
Figure 1 The influence of large hepatitis D antigen in activating oncogenic pathways.
JAK: Janus kinase; SRC: Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src; TRADD: Tumor necrosis factor receptor type 1-associated DEATH domain protein; FADD: Fas-associated protein with death domain; TRAF2: TNF receptor associated factor 2; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; RIP: Receptor-interacting protein; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; NF-κβ: Nuclear factor kappa beta; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; MEKK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase (MEK kinase); PKR: Protein kinase R; IKK: IêB kinase; CBP: CREB-binding protein.
- Citation: Abbas Z, Abbas M, Abbas S, Shazi L. Hepatitis D and hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol 2015; 7(5): 777-786
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v7/i5/777.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i5.777