Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Hepatol. Mar 27, 2015; 7(3): 377-391
Published online Mar 27, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i3.377
Published online Mar 27, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i3.377
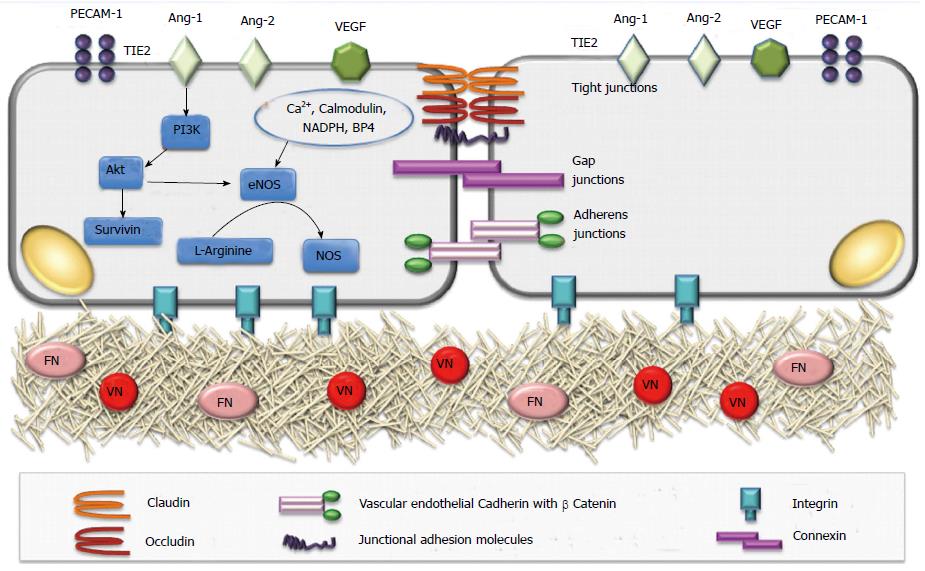
Figure 3 Structure and function of endothelium.
In endothelial cells an increase in Tie-2 signaling via the Ang-1 receptor initiates phosphorylation of Akt, which in turn phosphorylates eNOS and survivin. Enzymatic activity of eNOS is also regulated by calcium, calmodulin, NADPH, and BH4. The conversion of L-arginine to NO by eNOS leads to the cyclic-GMP-mediated relaxation of smooth muscle cells. Ang: Angiopoietin; BH4: 5,6,7,8 tetrahydrobiopterine; eNOS: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase; FN: Fibronectin; NO: Nitric oxide; PECAM-1: Platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1; VN: Vitronectin; Ang-1: Angiopoietin-1; Ang-2: Angiopoietin-2; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
- Citation: Elpek G&. Angiogenesis and liver fibrosis. World J Hepatol 2015; 7(3): 377-391
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v7/i3/377.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i3.377