Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Hepatol. Oct 18, 2015; 7(23): 2474-2481
Published online Oct 18, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i23.2474
Published online Oct 18, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i23.2474
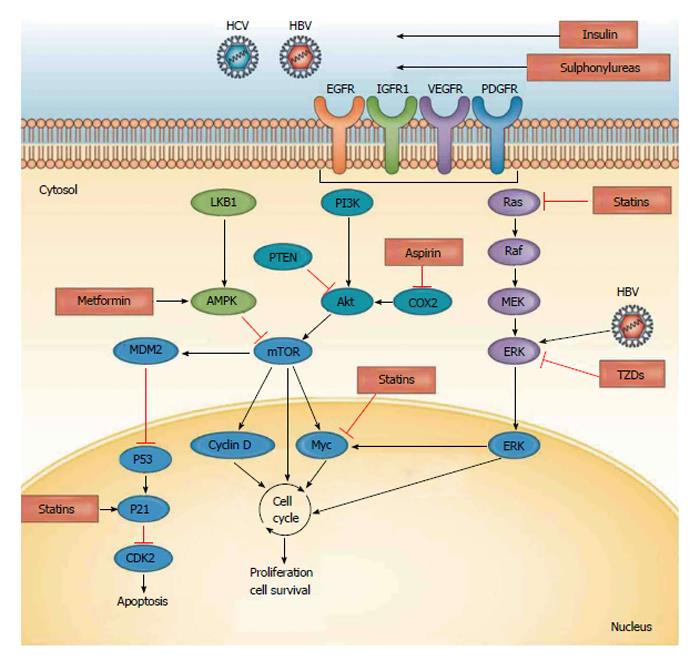
Figure 3 Pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma and targets for chemopreventive agents (cited from Singh et al[25], 2014).
AMPK: Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; IGFR1: Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1; MAPK: Ras mitogen-activated protein kinase; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; PTEN: Phosphatase/Tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10; P53: A tumor suppressor protein; P21: Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 inhibitor; CDK2: Cyclin-dependent kinase 2; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase protein; MEK: Minase that phosphorylate mitogen activated protein (MAP); PDGFR: Platelet derived growth factor receptor; VEGFR: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor; IGFR1: Insulin like growth factor receptor 1; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; Ras: Prototypical member of the RAS superfamily of proteins; Raf: A MAP kinase kinase kinase (a serine/threonine specific kinase); Akt: A protein kinase family of genes involved in regulating cell survival.
- Citation: Khattab M, Fouad M, Ahmed E. Role of biomarkers in the prediction and diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol 2015; 7(23): 2474-2481
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v7/i23/2474.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i23.2474