Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
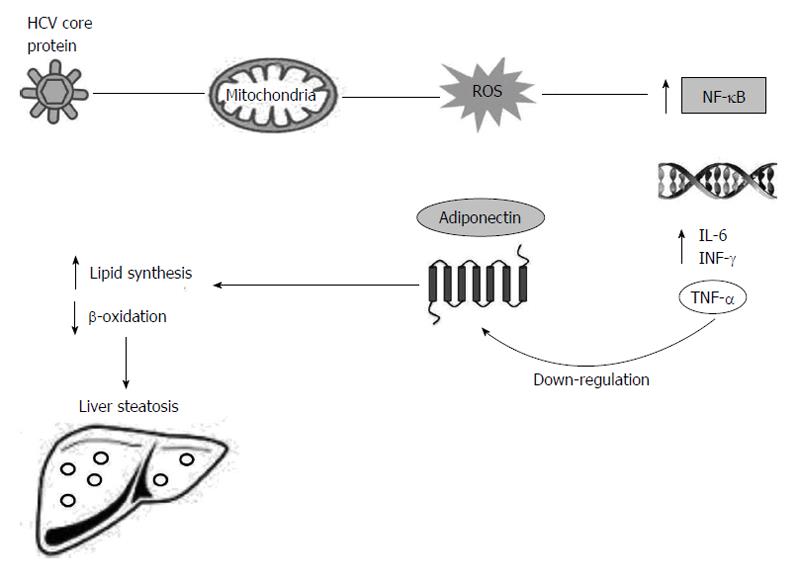
Figure 2 Liver steatosis induced by down-regulation of adiponectin and its receptor in chronic hepatitis C virus infection.
HCV core protein associated with the mitochondria leads to increased ROS that activates NF-κB. As a consequence of NF-κB activation, expression of a variety of cytokines is increased, including TNF-α, IL-6 and INF-γ. TNF-α modulates adipocytes and induces reduction in the production of adiponectin and its receptor. Reduced levels of adiponectin induce the increase in the synthesis of free fatty acids and reduce β-oxidation, causing liver steatosis in the HCV chronic infected patients. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; IL: Interleukin; IFN-γ: Interferon-γ; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor α; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
- Citation: Peta V, Torti C, Milic N, Focà A, Abenavoli L. Adiponectin serum level in chronic hepatitis C infection and therapeutic profile. World J Hepatol 2015; 7(1): 44-52
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v7/i1/44.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i1.44