Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Hepatol. Jan 27, 2015; 7(1): 121-126
Published online Jan 27, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i1.121
Published online Jan 27, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i1.121
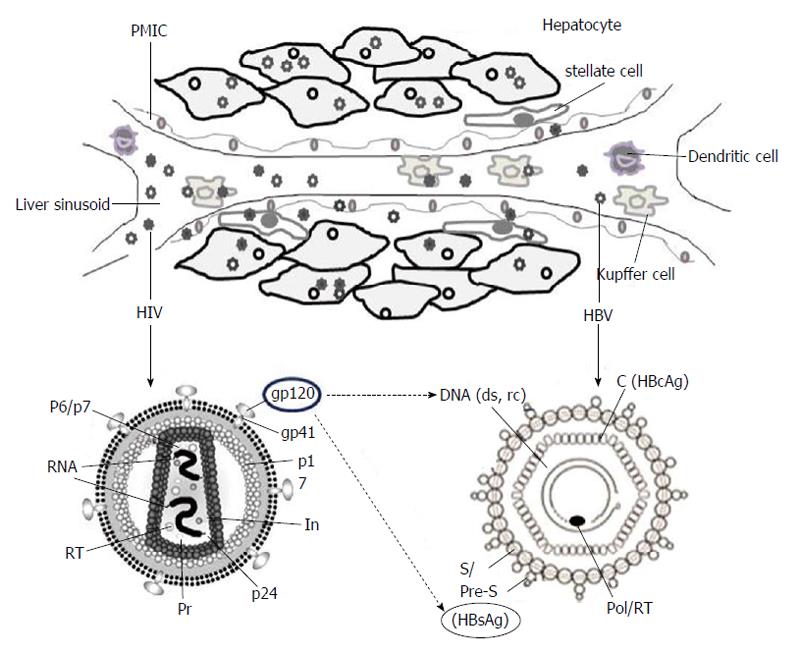
Figure 1 A cartoon depiction of hepatitis B virus and human immunodeficiency virus co-infection of liver.
Intracellular locations of the two viruses in hepatocytes, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, Kupffer cells, portal mononuclear inflammatory cells, stellate cells, dendritic cells and Kupffer cells are shown (upper panel). The structural and genomic organizations of HIV and HBV indicating the probable trans-regulation of HBV-DNA and HBsAg by HIVgp120 (lower panel). PMIC: Portal mononuclear inflammatory cell; HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; HBcAg: Hepatitis B core antigen; RT: HIV reverse-transcriptase.
- Citation: Parvez MK. HBV and HIV co-infection: Impact on liver pathobiology and therapeutic approaches. World J Hepatol 2015; 7(1): 121-126
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v7/i1/121.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i1.121