Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Hepatol. Jul 27, 2014; 6(7): 477-485
Published online Jul 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i7.477
Published online Jul 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i7.477
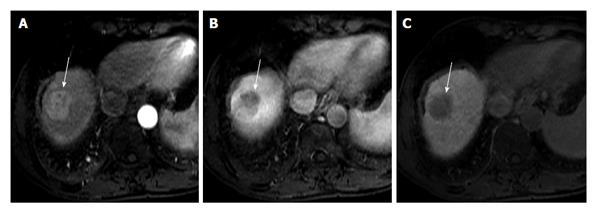
Figure 3 Imaging features of a typical hepatocellular carcinoma.
Axial magnetic resonance images show a hypervascular lesion in the arterial phase (A, white arrow), located in the top of the liver, with wash-out clearly in the portal venous phase (B, white arrow). This enhancement pattern represents the typical morphological hallmark of hepatocellular carcinoma. The nodule has an increased arteriolar supply and reduced portal vascularization. In hepatobiliary phase, the lesion appears hypointense to the surrounding liver parenchyma.
- Citation: Palmucci S. Focal liver lesions detection and characterization: The advantages of gadoxetic acid-enhanced liver MRI. World J Hepatol 2014; 6(7): 477-485
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v6/i7/477.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v6.i7.477