Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Hepatol. Apr 27, 2014; 6(4): 188-198
Published online Apr 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i4.188
Published online Apr 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i4.188
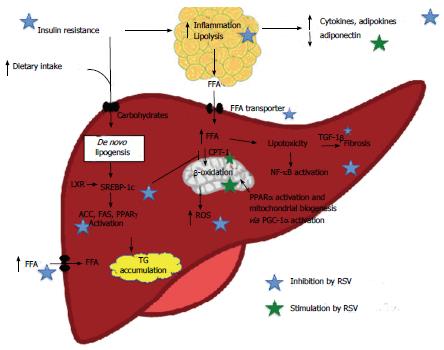
Figure 1 Proposed resveratrol effects on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease pathogenesis, AMP-activated protein kinase and silent information regulation-2 homolog 1 dependent and non-dependent mechanisms.
Evidence of in vivo effect demonstrated especially a RSV-mediated inhibition of adipose tissue lipolysis, inhibition of hepatic de novo lipogenesis and an increase in FA β-oxidation. ACC: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; CPT-1: Carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1; FAS: Fatty acid synthase; FFA: Free fatty acids; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; PGC-1α: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 α; PPARγ/α: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ/α; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; SREBP-1c: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c; TG: Triglyceride; TGF-1β: Tumor growth factor 1β.
- Citation: Heebøll S, Thomsen KL, Pedersen SB, Vilstrup H, George J, Grønbæk H. Effects of resveratrol in experimental and clinical non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Hepatol 2014; 6(4): 188-198
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v6/i4/188.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v6.i4.188