Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2014; 6(12): 870-879
Published online Dec 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i12.870
Published online Dec 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i12.870
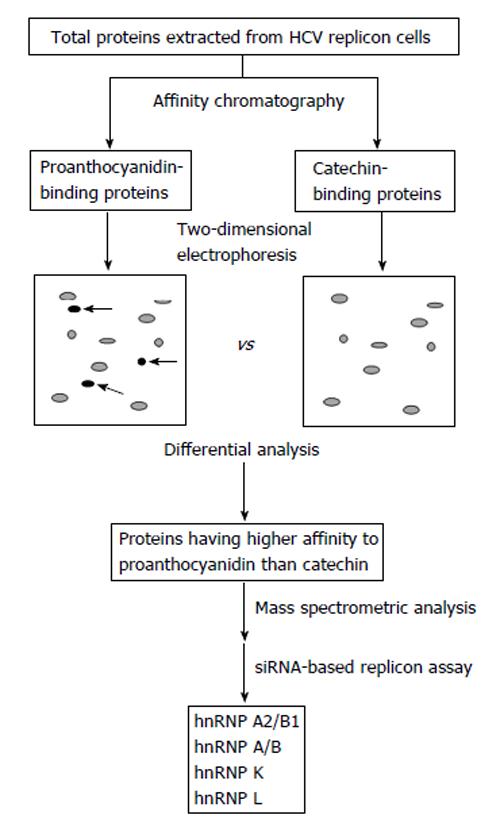
Figure 4 Identification strategy of candidate proteins involved in the proanthocyanidin-mediated inhibition of hepatitis C virus subgenomic expression[13].
Total proteins were extracted from hepatitis C virus (HCV) replicon cells and then proanthocyanidin-binding and catechin-binding proteins were purified by affinity chromatography using sepharose beads coupled with proanthocyanidin and catechin, respectively. Purified proteins were separated by two-dimensional electrophoresis followed by detecting spots of proteins having higher affinity to proanthocyanidin than catechin (arrows). Mass spectrometric analysis and further screening by a siRNA-based replicon assay showed that hnRNP A2/B1, A/B, K, and L are candidate proteins involved in the oligomeric proanthocyanidin-mediated inhibition of HCV subgenomic expression. hnRNP: Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein.
- Citation: Ishida YI, Takeshita M, Kataoka H. Functional foods effective for hepatitis C: Identification of oligomeric proanthocyanidin and its action mechanism. World J Hepatol 2014; 6(12): 870-879
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v6/i12/870.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v6.i12.870