Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Hepatol. Nov 27, 2014; 6(11): 793-799
Published online Nov 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i11.793
Published online Nov 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i11.793
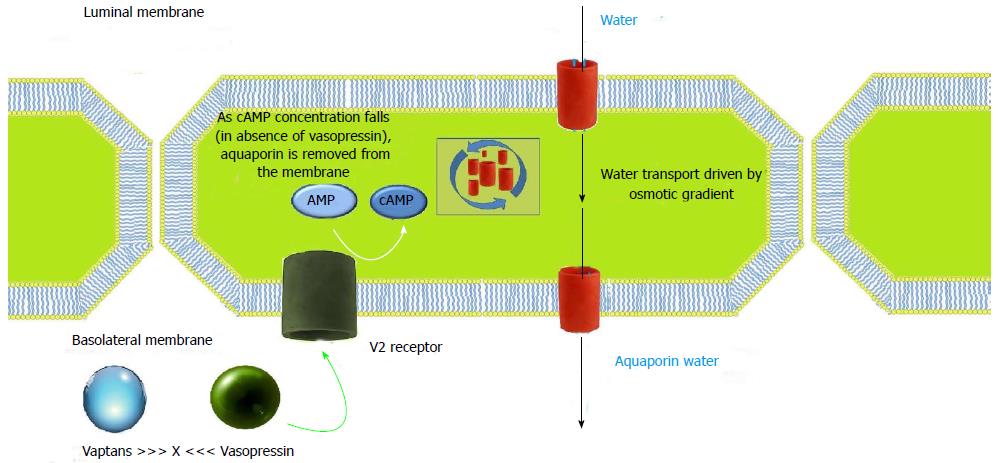
Figure 3 Mechanism of action of vaptans.
In physiologic conditions, binding of arginine vasopressin to its receptor, raises introcytoplasmatic levels of cyclic adenosine monophosphate, thus resulting in increased expression of aquaporin on the luminal membrane of principal cells in collecting duct. Therefore, free water move down gradient via aquaporin from ductal lumen to blood. Vaptans, by blocking binding of arginine vasopressin to its receptor, inhibit water reabsorption. cAMP: Cyclic adenosine mono-phosphate.
- Citation: Facciorusso A, Amoruso A, Neve V, Antonino M, Prete VD, Barone M. Role of vaptans in the management of hydroelectrolytic imbalance in liver cirrhosis. World J Hepatol 2014; 6(11): 793-799
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v6/i11/793.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v6.i11.793