Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Hepatol. Oct 27, 2014; 6(10): 716-737
Published online Oct 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i10.716
Published online Oct 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i10.716
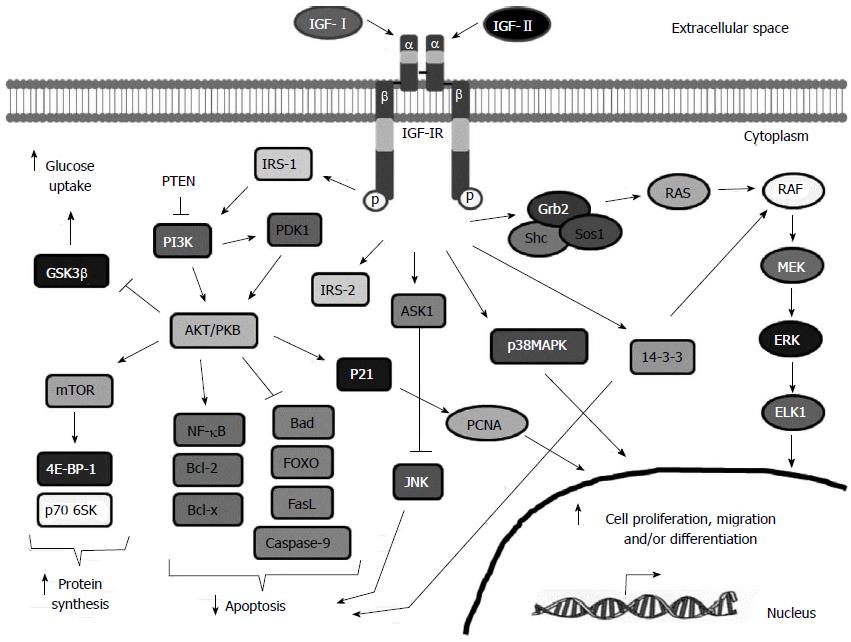
Figure 2 Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling pathway.
Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), IGF-II and to a lesser extent, insulin, can bind to IGF-IR and promote a conformational change that leads to the autophosphorylation and activation of the IGF-IR. Phosphorylated receptor recruits specific docking proteins including IRS1-4, Shc and 14-3-3 which trigger mainly the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and the RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathways. Activation of the IGF-IR induces protein and glycogen synthesis, glucose uptake, cell proliferation, migration and survival and cell differentiation depending on the cell type. See text for more details. GSK-3β: Glycogen synthase kinase-3; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase; AKT/PKB: Protein kinase B; NFKB: Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma 2; IRS-2: Insulin receptor substrate 2; FOXO: Forkhead box protein O1; PCNA: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; RAF: Rapidly Accelerated Fibrosarcoma; MEK: Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase; ERK: Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase; ELK1: ETS-Like kinase; ELK1: ETS-Like kinase.
- Citation: Enguita-Germán M, Fortes P. Targeting the insulin-like growth factor pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol 2014; 6(10): 716-737
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v6/i10/716.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v6.i10.716