Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Hepatol. Oct 27, 2014; 6(10): 716-737
Published online Oct 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i10.716
Published online Oct 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i10.716
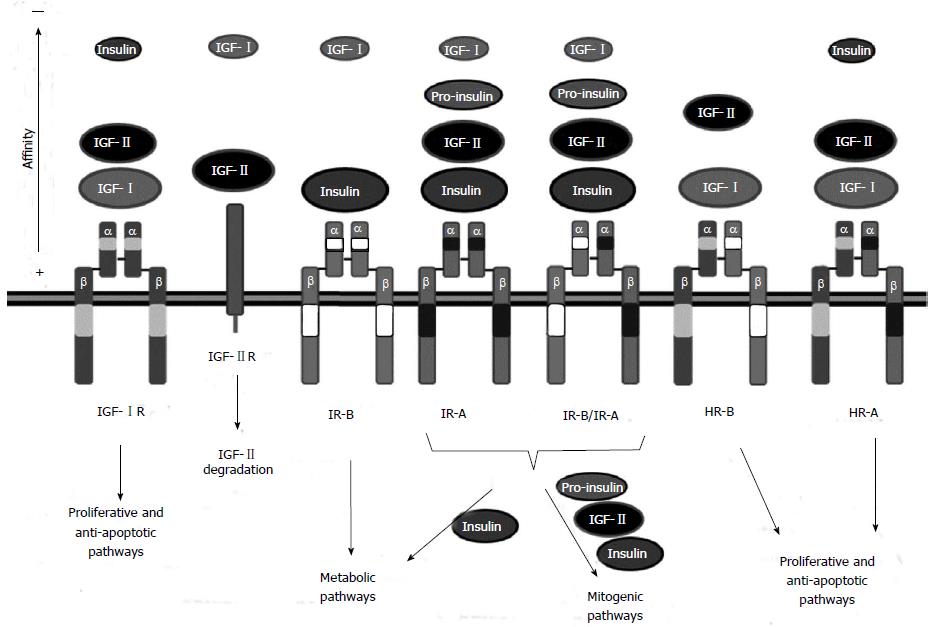
Figure 1 Insulin-like growth factor receptors and their ligands.
The insulin-like growth factor (IGF) system is composed of three receptors: IGF-IR, IGF-IIR and insulin receptor (IR). IGF-IR is the main receptor of the IGF system. It can bind IGF-I and IGF-II with high affinity. IGF-IIR is a negative regulator of the pathway that binds IGF-II and promotes IGF-II degradation. Finally, IR mediates insulin signaling. Two IR isoforms exist: the adult IR-B isoform that binds insulin and the fetal IR-A isoform, that can bind IGF-II in addition to insulin promoting mitogenic signaling. The IR-A isoform is commonly overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). IR isoforms can form IR-A/IR-B hybrids which behave as IR-A receptors. Moreover, HR-A or HR-B hybrid receptors can be formed between IGF-IR and IR-A or IR-B respectively. These hybrid receptors lack high affinity binding to insulin and act, similar to the IGF-IR receptor, promoting proliferation and survival.
- Citation: Enguita-Germán M, Fortes P. Targeting the insulin-like growth factor pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol 2014; 6(10): 716-737
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v6/i10/716.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v6.i10.716