Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Hepatol. Aug 27, 2013; 5(8): 417-424
Published online Aug 27, 2013. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v5.i8.417
Published online Aug 27, 2013. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v5.i8.417
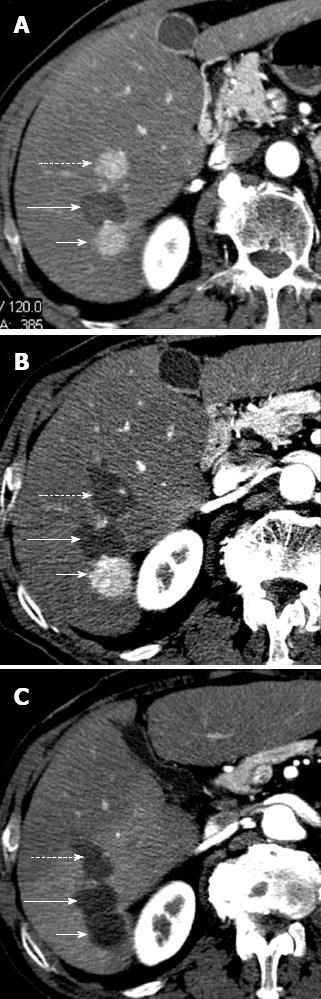
Figure 3 Hepatocellular carcinoma after multiple radiofrequency ablations.
A: Arterial phase computed tomography (CT) obtained 8 mo after radiofrequency ablation shows two new enhancing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) nodules located anteriorly (dotted arrow) and posteriorly (short arrow) to ablated HCC (long arrow). These findings suggest occurrence of new HCC nodules; B: Arterial phase CT obtained 2 mo after additional radiofrequency (RF) ablation shows that HCC nodule located anteriorly (dotted arrow) has been replaced by a hypoattenuating, non enhancing area (arrow) that is larger than preexisting tumor. These findings suggest complete necrosis. Posteriorly located HCC (short arrow) increased in size; C: Arterial phase CT obtained 2 mo after posterior. HCC had been replaced by a hypoattenuating, nonenhancing ablation area as a result of additional RF ablation. This example shows that RF ablation is a repeatable procedure.
- Citation: Agnello F, Salvaggio G, Cabibbo G, Maida M, Lagalla R, Midiri M, Brancatelli G. Imaging appearance of treated hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol 2013; 5(8): 417-424
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v5/i8/417.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v5.i8.417