Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Hepatol. Apr 27, 2013; 5(4): 206-213
Published online Apr 27, 2013. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v5.i4.206
Published online Apr 27, 2013. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v5.i4.206
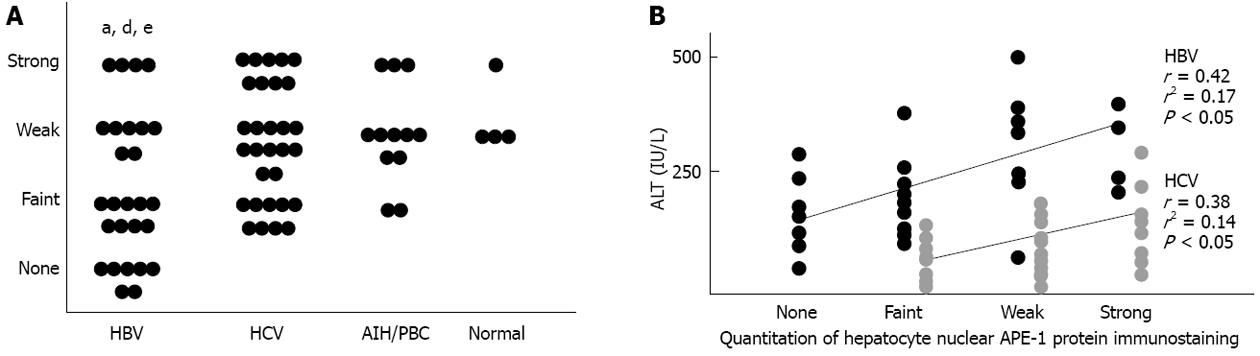
Figure 2 Quantitation of hepatocyte nuclear apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 protein immunostaining.
A: The percentage of positive hepatocellular nuclei throughout the slide was consistently 80%-100%, regardless of the etiology of chronic liver disease, while the staining intensity was lower in hepatitis B virus (HBV) group than in hepatitis C virus (HCV), autoimmune hepatitis (AIH)/primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) and normal groups (aP < 0.05 vs HCV, dP < 0.01 vs AIH/PBC, eP < 0.05 vs normal); B: The staining intensity of hepatocytic nuclear apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE-1) protein was positively correlated with serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels in the HBV (r = 0.42, P < 0.05) and HCV groups (r = 0.38, P < 0.05).
- Citation: Sumiyoshi S, Kobayashi Y, Kawamura K, Kawata K, Nakamura H. Differential expression of hepatic apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1, a DNA repair enzyme, in chronic hepatitis. World J Hepatol 2013; 5(4): 206-213
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v5/i4/206.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v5.i4.206