Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Hepatol. Oct 27, 2013; 5(10): 568-576
Published online Oct 27, 2013. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v5.i10.568
Published online Oct 27, 2013. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v5.i10.568
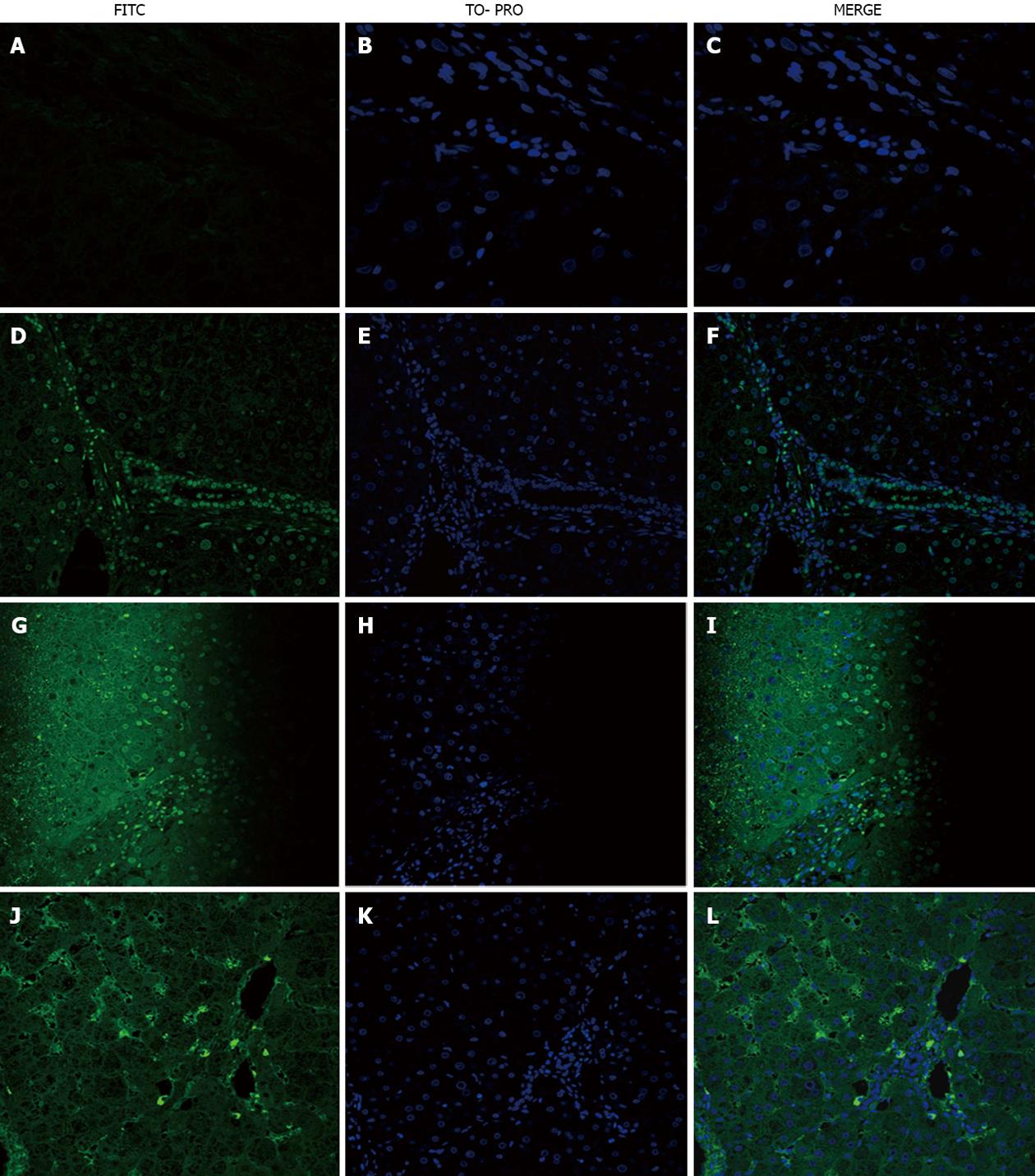
Figure 1 Immunofluorescence of primary biliary cirrhosis sections incubated with primary biliary cirrhosis serum and fluorescein isothiocyanate -conjugated IgG or IgM secondary antibody.
A-C: Negative control incubated with IgG secondary antibody; D-F: Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) section incubated with homologous PBC serum and IgG secondary antibody, showing staining of cholangiocytes, sinusoidal cells (weak staining) and mononuclear cells, probably lymphocytes; G-I: PBC section incubated with heterologous PBC serum and IgG secondary antibody, showing nuclear and cytoplasmic staining of hepatocytes and lymphocytes; J-L: PBC section incubated with homologous PBC serum and IgM secondary antibody, showing cytoplasmic staining of sinusoidal cells and lymphocytes. Magnification × 200. FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate.
- Citation: Sfakianaki O, Tzardi M, Voumvouraki A, Afgoustaki A, Koulentaki M, Kouroumalis E. Presence of disease specific autoantibodies against liver sinusoidal cells in primary biliary cirrhosis. World J Hepatol 2013; 5(10): 568-576
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v5/i10/568.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v5.i10.568