Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Hepatol. Apr 27, 2012; 4(4): 119-128
Published online Apr 27, 2012. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v4.i4.119
Published online Apr 27, 2012. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v4.i4.119
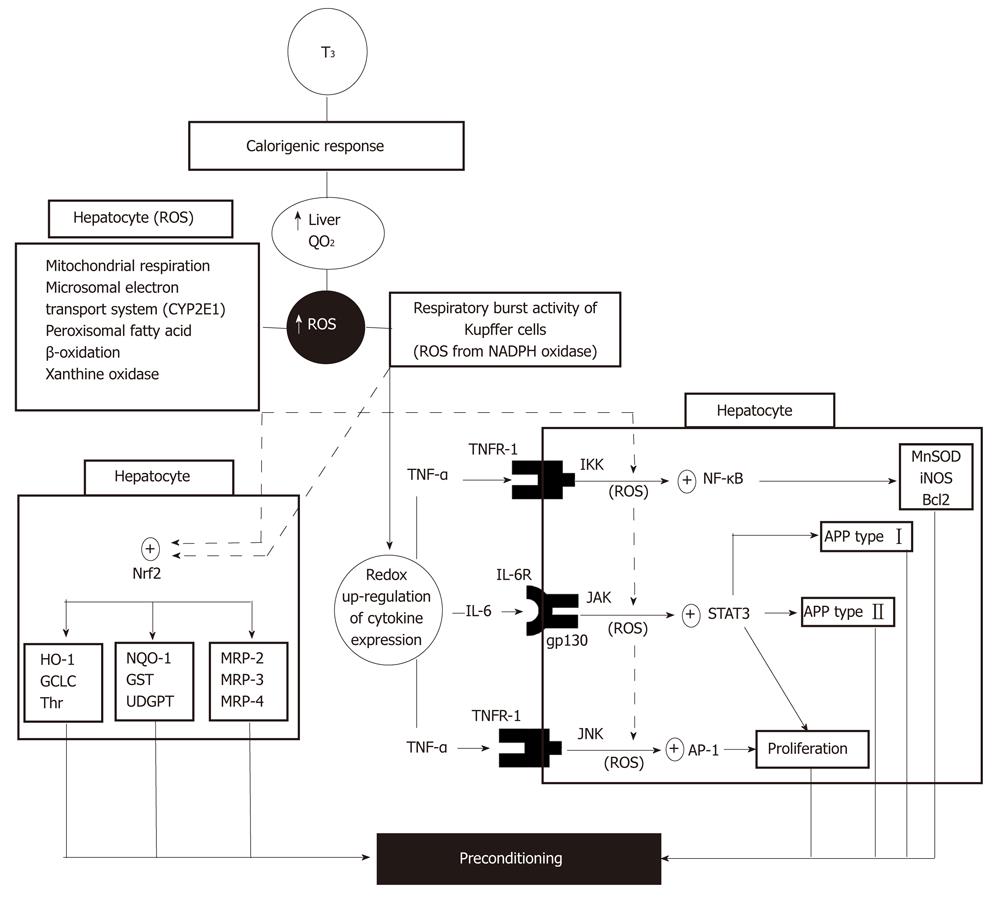
Figure 1 Redox signaling in T3 liver preconditioning is mediated by activation of transcription factors nuclear factor-κB, activating protein 1, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 triggering antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, acute-phase and proliferative responses.
AP-1: Activating protein 1; APP: Acute-phase protein; CYP2E1: Cytochrome P450 isoform 2E1; GCLC: Glutamate cysteine ligase catalytic subunit; GST: Glutathione-S-transferase; HO-1: Heme-oxygenase 1; IKK: Inhibitor of IκB kinase; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-6R: Interleukin-6 receptor; JAK: Janus kinase; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; MnSOD: Manganese superoxide dismutase; MRP: Multidrug resistance protein; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; NQO-1: NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 1; Nrf2: Nuclear factor-erythroid 2 related factor 2; QO2: Rate of oxygen consumption; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; Thr: Thioredoxin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; TNFR1: Tumor necrosis factor-α receptor 1; UDPGT: UDP-glucuronyl transferase.
- Citation: Fernández V, Tapia G, Videla LA. Recent advances in liver preconditioning: Thyroid hormone, n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids and iron. World J Hepatol 2012; 4(4): 119-128
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v4/i4/119.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v4.i4.119