Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2012; 4(12): 342-355
Published online Dec 27, 2012. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v4.i12.342
Published online Dec 27, 2012. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v4.i12.342
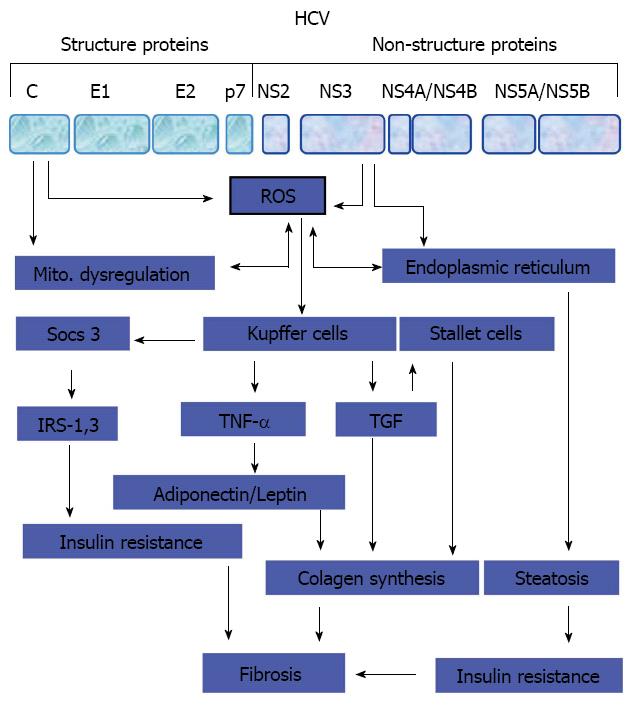
Figure 2 Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C infected patients.
Potential mechanisms that thought be involved in the regulation of hepatitis C virus -associated hepatic fibrosis. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; IRS: Insulin receptor substrate; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; TGF: Transforming growth factor.
- Citation: Selimovic D, El-Khattouti A, Ghozlan H, Haikel Y, Abdelkader O, Hassan M. Hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: An insight into molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. World J Hepatol 2012; 4(12): 342-355
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v4/i12/342.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v4.i12.342