Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Hepatol. Nov 27, 2012; 4(11): 322-326
Published online Nov 27, 2012. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v4.i11.322
Published online Nov 27, 2012. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v4.i11.322
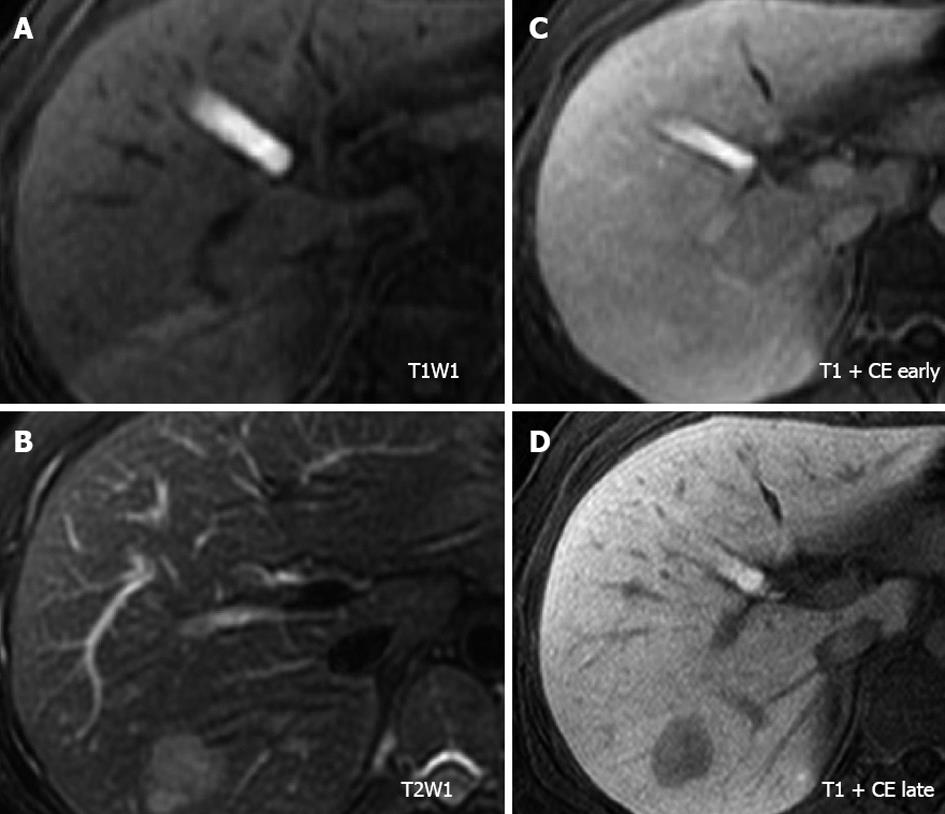
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging of the tumor.
A: The tumor showed an iso-intensity with the surrounding liver parenchyma on T1-weighted imaging; B: The tumor was visualized as a heterogeneous hyper-intense mass on T2-weighted imaging; C and D: After gadolinium ethoxybenzyl diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid enhancement, the tumor was discernible in the arterial phase and was clearly detected as a hypo-intense lesion in the hepato-biliary phase on T1-weighted imaging. CE: Contrast enhanced.
- Citation: Inaba K, Sakaguchi T, Kurachi K, Mori H, Tao H, Nakamura T, Takehara Y, Baba S, Maekawa M, Sugimura H, Konno H. Hepatocellular adenoma associated with familial adenomatous polyposis coli. World J Hepatol 2012; 4(11): 322-326
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v4/i11/322.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v4.i11.322