Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Hepatol. Oct 27, 2012; 4(10): 288-290
Published online Oct 27, 2012. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v4.i10.288
Published online Oct 27, 2012. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v4.i10.288
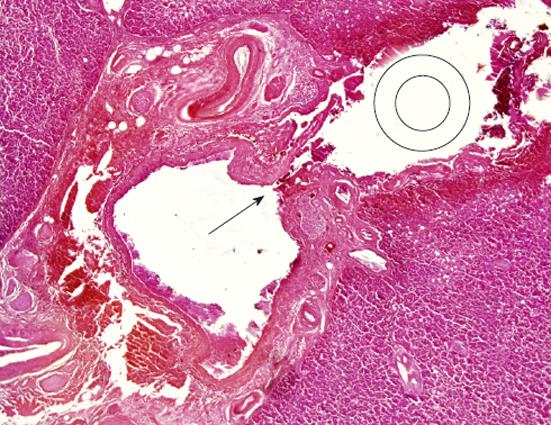
Figure 3 Microscopic specimen at the crossover site of intrahepatic connective tissue and the percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder drainage pathway (hematoxylin-eosin staining).
There is a rupture of the arterial wall near the catheter pathway and intrahepatic bleeding along the percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder drainage pathway. The arrow dead shows the point where the intrahepatic artery is ruptured, and the double circle shows a cross section of the catheter on the pathway (C).
- Citation: Ihama Y, Fukazawa M, Ninomiya K, Nagai T, Fuke C, Miyazaki T. Peritoneal bleeding due to percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder drainage: An autopsy report. World J Hepatol 2012; 4(10): 288-290
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v4/i10/288.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v4.i10.288