Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
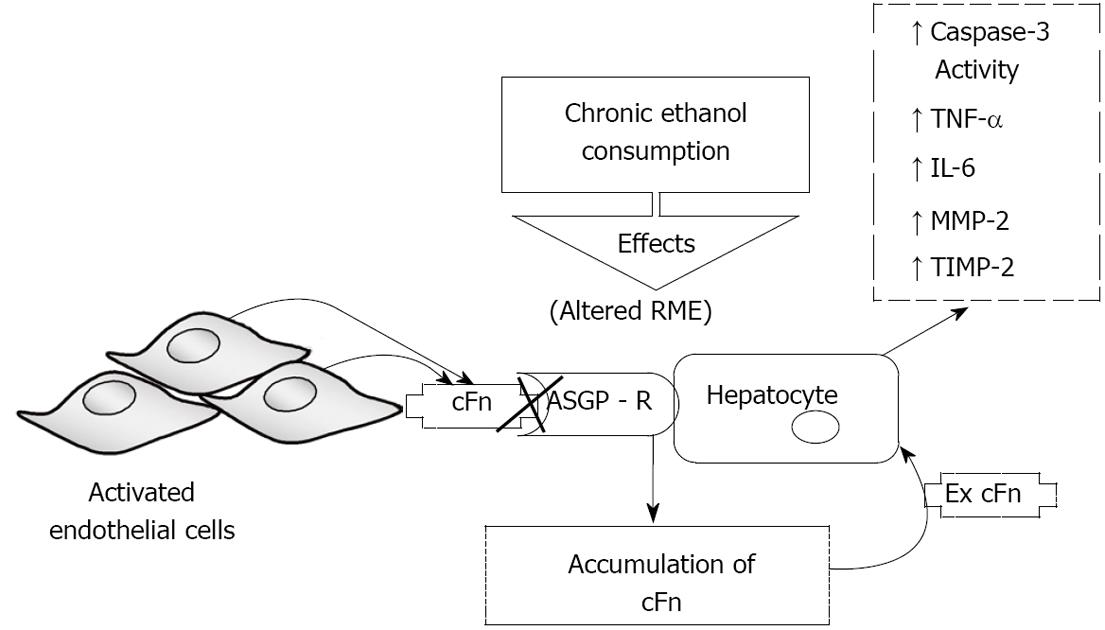
Figure 7 Schematic representation of the proposed model of ethanol-induced liver injury linking altered asialoglycoprotein receptor clearance of cellular fibronectin with hepatocyte activation by the accumulating protein.
Subsequently, there is an increase in caspase-3 activity and an elevated secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), as well as secretion of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and its corresponding inhibitor tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2). RME: receptor-mediated endocytosis; ASGP-R: asialoglycoprotein receptor.
- Citation: Aziz-Seible RS, McVicker BL, Kharbanda KK, Casey CA. Cellular fibronectin stimulates hepatocytes to produce factors that promote alcohol-induced liver injury. World J Hepatol 2011; 3(2): 45-55
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v3/i2/45.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v3.i2.45