Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
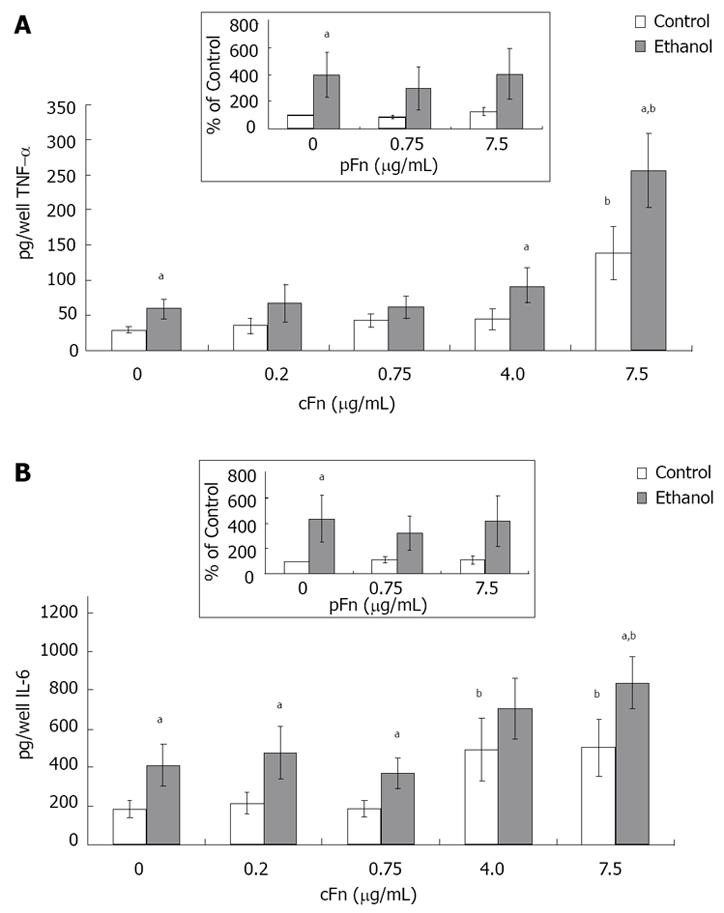
Figure 6 Secretion of cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 by cultured hepatocytes isolated from the livers of rats that were pair-fed control and ethanol diets and stimulated with cellular fibronectin.
Hepatocytes were cultured in the presence of different concentrations of exogenous cultured hepatocytes (cFn) (0 μg/mL, 0.2 μg/mL, 0.75 μg/mL, 4.0 μg/mL and 7.5 μg/mL) for 20 h. After this time, the level of each cytokine (pg/well) released by the cells into the culture supernatant was determined by ELISA, as described in Material and Methods. In the presence of 7.5 μg/mL cFn, cells from both control and ethanol-fed animals released elevated levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) (A) and Interleukin-(IL)-6 (B) compared with corresponding untreated cells, with hepatocytes from ethanol-fed rats secreting significantly higher levels of both cytokines compared with controls. Plasma fibronectin treatment produced no effect on either cell type (inserts, A and B). Data are represented as means ± SEM. Ethanol values significantly different from those of the control are expressed as aP < 0.05, and treatment significantly different from untreated cultures is expressed as bP < 0.05. (n = 8 - 15 experiments).
- Citation: Aziz-Seible RS, McVicker BL, Kharbanda KK, Casey CA. Cellular fibronectin stimulates hepatocytes to produce factors that promote alcohol-induced liver injury. World J Hepatol 2011; 3(2): 45-55
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v3/i2/45.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v3.i2.45