Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
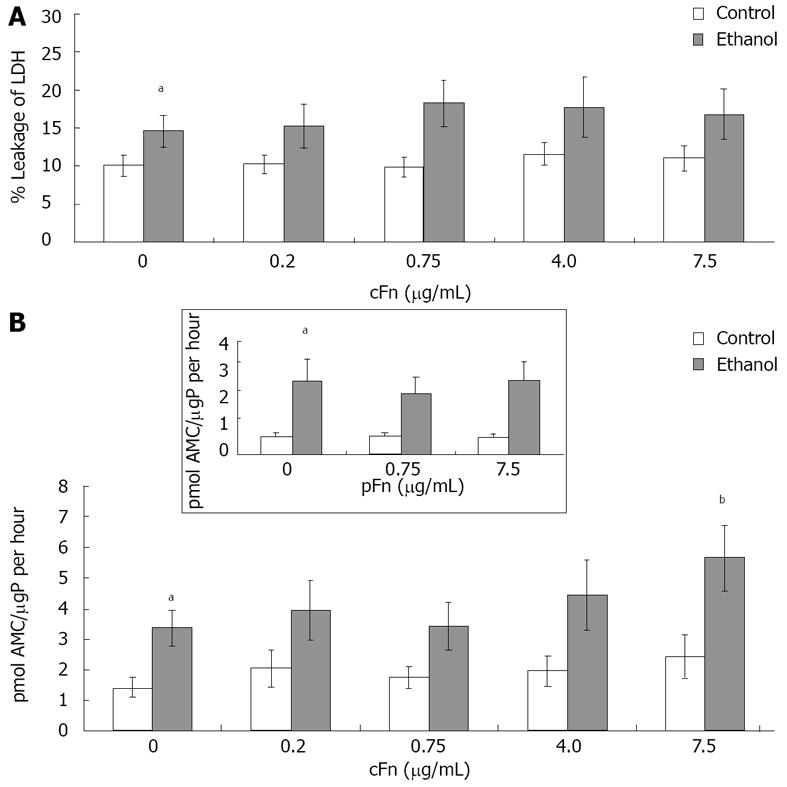
Figure 3 Effect of cellular fibronectin on hepatocyte viability.
A: Percentage leakage of the cytosolic lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) enzyme into the cell culture supernatant was used to test for severe irreversible cell damage (necrosis) as described in Material and Methods. Incidence of necrosis was consistently higher in cultured cells from ethanol-fed animals (n = 8 - 12); B: Caspase-3 activity in the cells was determined as described in Material and Methods. Basal level caspase-3 activity was significantly higher in hepatocytes from ethanol-fed animals when compared with controls. Enzyme activity is presented as picomoles of fluorogenic AMC product released upon cleavage of the caspase-3 substrate Ac-DEVD-AMC, per µg protein in the cell lysate in an hour. At the higher dose of exogenous cellular fibronectin (cFn) (7.5 μg/mL), caspase-3 activity was significantly induced in cells from the ethanol-fed animals. No changes were seen in the control cells (n = 5 - 14). Plasma fibronectin exhibited no effect on either cell type (inset). Data are represented as means ± SEM. Ethanol values significantly different from those of the control are expressed as aP < 0.05, and treatment significantly different from untreated cultures is expressed as bP < 0.05. μgP: μg protein.
- Citation: Aziz-Seible RS, McVicker BL, Kharbanda KK, Casey CA. Cellular fibronectin stimulates hepatocytes to produce factors that promote alcohol-induced liver injury. World J Hepatol 2011; 3(2): 45-55
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v3/i2/45.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v3.i2.45