Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Hepatol. Nov 27, 2010; 2(11): 395-400
Published online Nov 27, 2010. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v2.i11.395
Published online Nov 27, 2010. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v2.i11.395
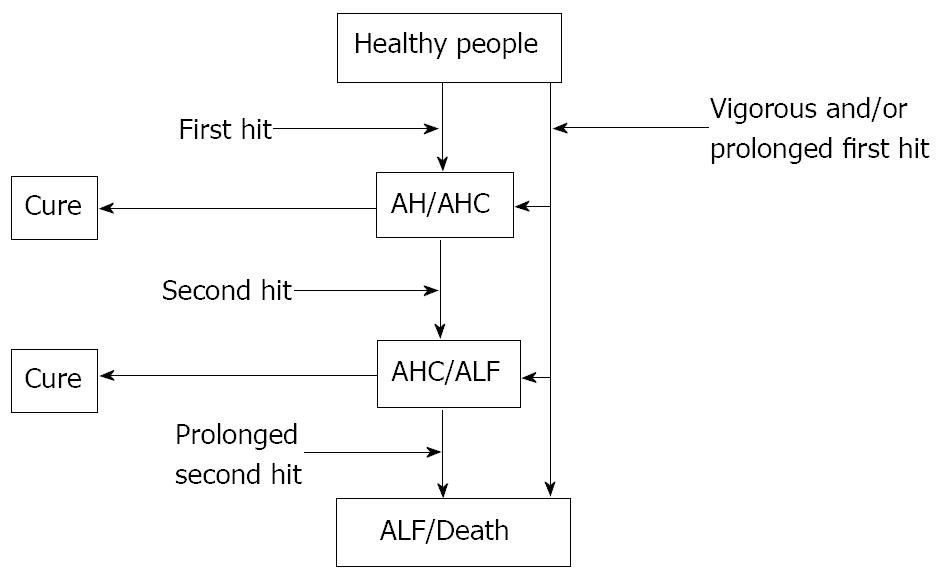
Figure 1 Overview of acute liver failure.
Various triggers may directly harm the hepatocytes as a first hit, although this is usually not strong enough to lead to acute liver failure (ALF). In some patients who experience a first hit, over-activation of macrophages occurs in the liver as a second hit which leads to microcirculatory disturbances in the liver and massive hepatocyte death. The activated macrophages spontaneously decline in some patients but, if this activity is prolonged, the risk of death is substantially increased. Overall, the degree of liver damage is determined by the sum of the first and second hit. AH: acute hepatitis; AHC: acute hepatitis with coagulopathy.
- Citation: Kotoh K, Kato M, Kohjima M, Nakamuta M, Enjoji M. A new treatment strategy for acute liver failure. World J Hepatol 2010; 2(11): 395-400
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v2/i11/395.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v2.i11.395