Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Mar 27, 2025; 17(3): 104167
Published online Mar 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i3.104167
Published online Mar 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i3.104167
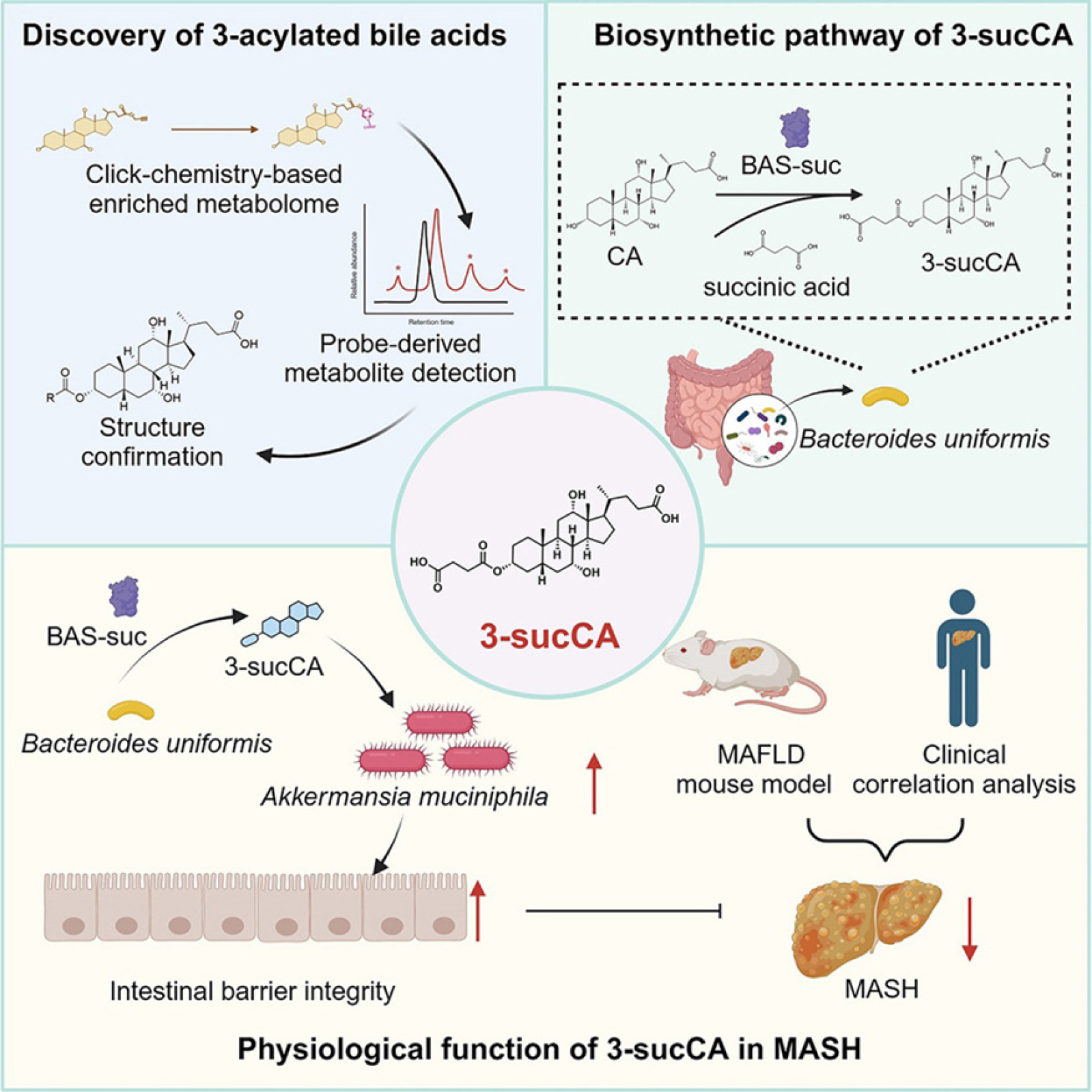
Figure 2 The bile acid 3-succinylated cholic acid, which is produced from microorganisms, is identified via a click chemistry approach.
The production of 3-succinylated cholic acid (3-sucCA) is mediated by Bacteroides uniformis-expressed bile acid acyl synthetase for succinyl. In patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease, 3-sucCA has a negative correlation with liver damage 3-sucCA reduces metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis in mice by encouraging the growth of Akkermansia muciniphila. 3-sucCA: 3-succinylated cholic acid; BAS-suc: Bile acid acyl synthetase for succinyl; MAFLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease; MASH: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis. Citation: Nie Q, Luo X, Wang K, Ding Y, Jia S, Zhao Q, Li M, Zhang J, Zhuo Y, Lin J, Guo C, Zhang Z, Liu H, Zeng G, You J, Sun L, Lu H, Ma M, Jia Y, Zheng MH, Pang Y, Qiao J, Jiang C. Gut symbionts alleviate MASH through a secondary bile acid biosynthetic pathway. Cell 2024; 187: 2717-2734.e33. Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc.
- Citation: Yakut A. Gut microbiota in the development and progression of chronic liver diseases: Gut microbiota-liver axis. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(3): 104167
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i3/104167.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i3.104167