Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Mar 27, 2025; 17(3): 103261
Published online Mar 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i3.103261
Published online Mar 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i3.103261
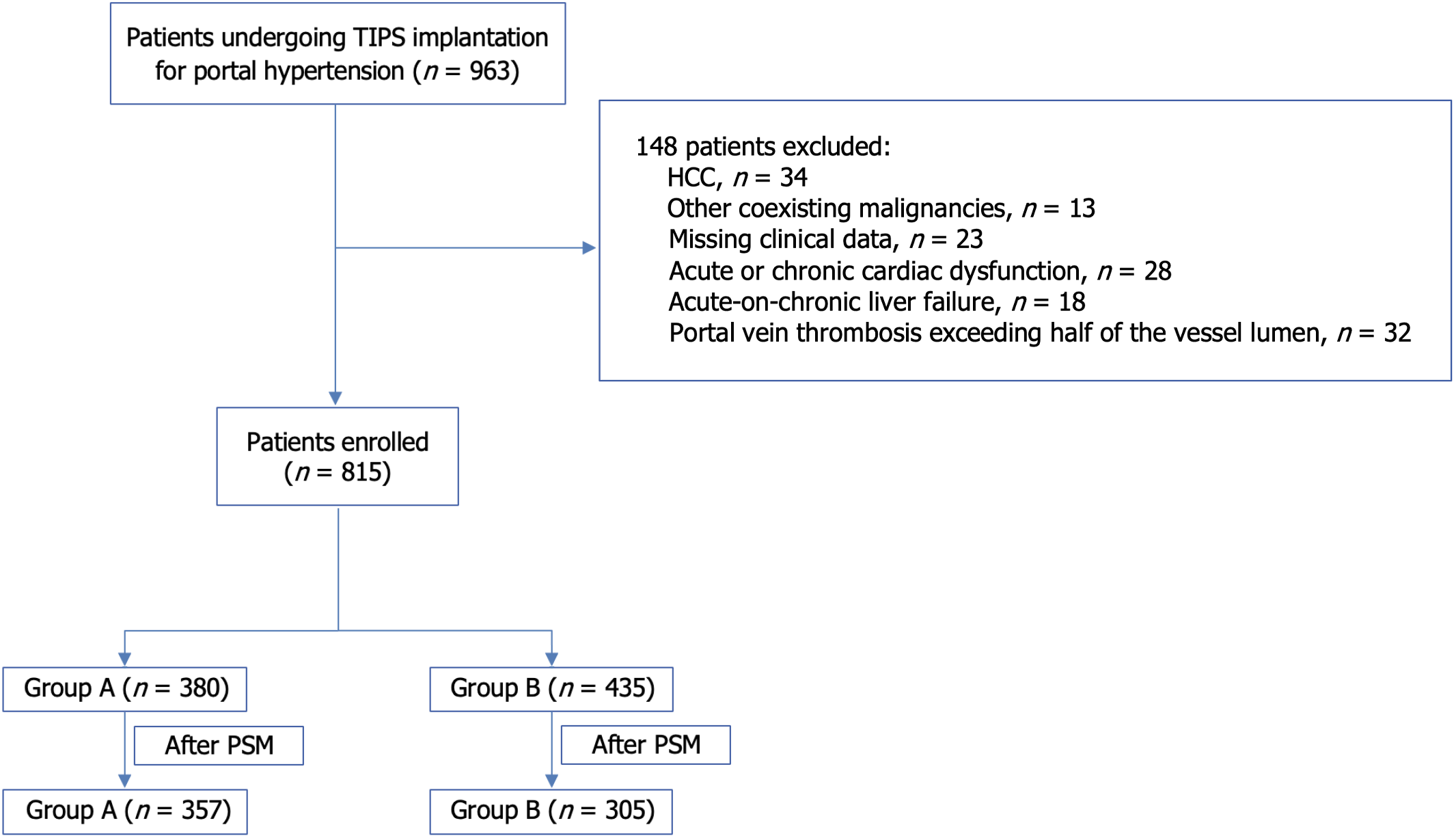
Figure 1 Study flowchart.
The flowchart illustrating the screening and grouping of 963 transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt-treated portal hypertension patients. A total of 148 patients were excluded whereas 815 were included. Patients were divided based on portal pressure gradient reduction into group A and group B, with 357 and 305 patients, respectively, after propensity score matching. TIPS: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; PSM: Propensity score matching.
- Citation: Wang ZB, Zhu B, Meng MM, Wu YF, Zhang Y, Li DZ, Tian H, Wang FC, Lv YF, Ye QX, Liu FQ. Effect of portal pressure gradient reduction on outcomes after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in portal hypertension patients. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(3): 103261
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i3/103261.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i3.103261