Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Mar 27, 2025; 17(3): 101340
Published online Mar 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i3.101340
Published online Mar 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i3.101340
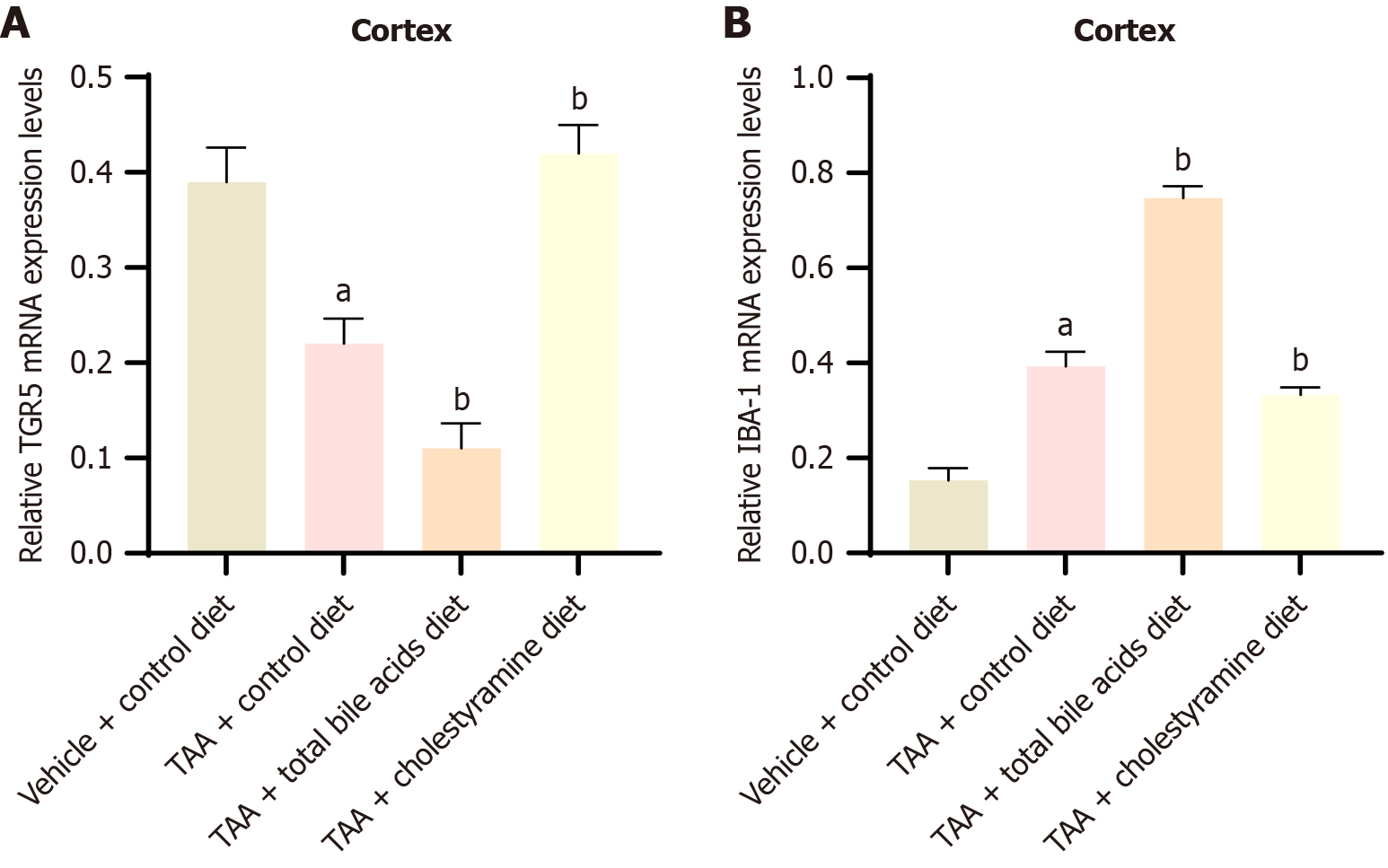
Figure 6 Takeda G protein-coupled receptor 5 and ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule-1 were measured by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (mean ± SD, n = 10).
A and B: The expression of Takeda G protein-coupled receptor 5 and ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule-1 in the cerebral cortex, respectively. aP < 0.05 compared with vehicle + control diet group; bP < 0.05 compared with thioacetamide group. TAA: Thioacetamide; TGR5: Takeda G protein-coupled receptor 5; IBA-1: Ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule-1.
- Citation: Ren C, Cha L, Huang SY, Bai GH, Li JH, Xiong X, Feng YX, Feng DP, Gao L, Li JY. Dysregulation of bile acid signal transduction causes neurological dysfunction in cirrhosis rats. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(3): 101340
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i3/101340.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i3.101340