Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Mar 27, 2025; 17(3): 101340
Published online Mar 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i3.101340
Published online Mar 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i3.101340
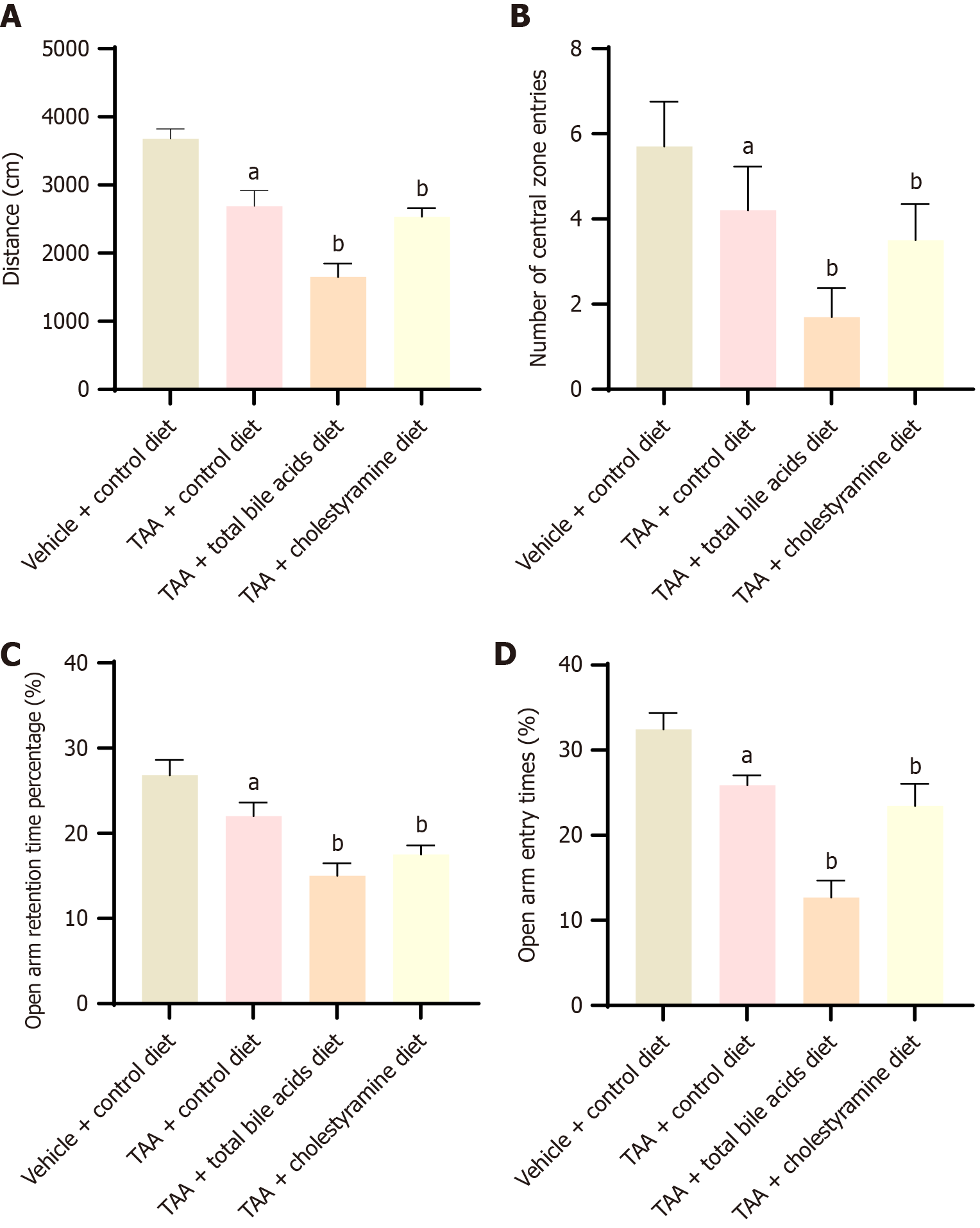
Figure 1 Thioacetamide-induced bile acid feeding in cirrhotic rats led to increased anxiety-like behavior (mean ± SD, n = 10).
A-D: The total distance of the open-field experiment, the number of central areas of the open open-field experiment, and the open arm of the elevated cross-experiment, percentage of entry times and percentage of residence time of open arm in elevated cross test. aP < 0.05 compared with vehicle + control diet group; bP < 0.05 compared with thioacetamide group. TAA: Thioacetamide.
- Citation: Ren C, Cha L, Huang SY, Bai GH, Li JH, Xiong X, Feng YX, Feng DP, Gao L, Li JY. Dysregulation of bile acid signal transduction causes neurological dysfunction in cirrhosis rats. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(3): 101340
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i3/101340.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i3.101340