Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Feb 27, 2025; 17(2): 99292
Published online Feb 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i2.99292
Published online Feb 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i2.99292
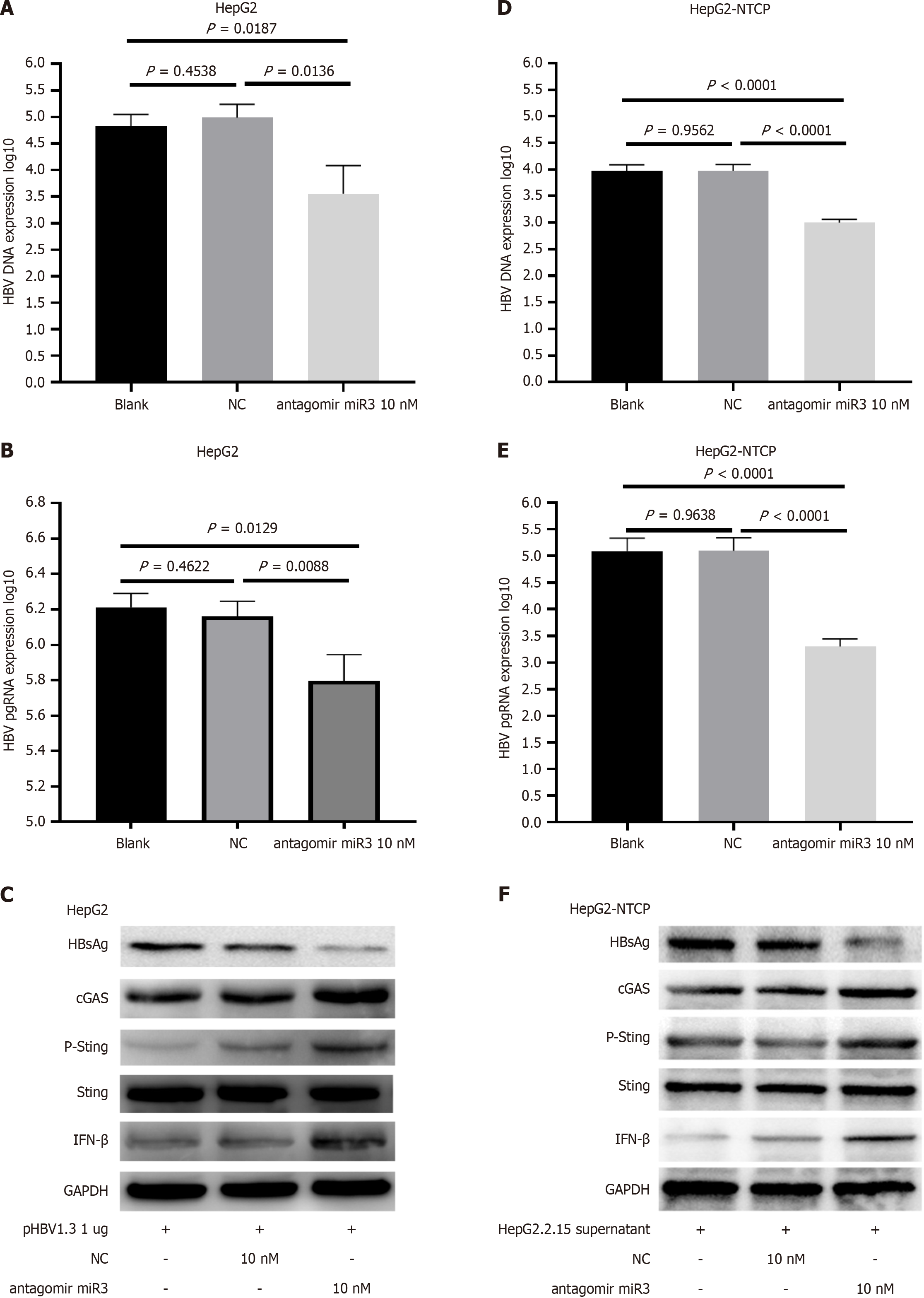
Figure 5 Hepatitis B virus-miR-3 antagomir inhibited hepatitis B virus replication.
A-C: HepG2 cells transfected with pHBV1.3 were treated with an HBV-miR-3 inhibitor for 72 hours, resulting in alterations in hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA (A), HBV pgRNA (B), and HBsAg (C); D-F: HepG2-NTCP cells were infected with HBV from HepG2.2.15 cell supernatant and treated with an HBV-miR-3 antagomir for 72 hours, resulting in alterations in HBV DNA (D), HBV pgRNA levels (E), and HBsAg (F). Each experiment was repeated three times. The data are presented as mean ± SD. NC: Negative control; HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
- Citation: Xu ZY, Gao JS, He Y, Xiao XQ, Gong GZ, Zhang M. Hepatitis B virus confers innate immunity evasion through hepatitis B virus-miR-3 down-regulation of cGAS-Sting-IFN signaling. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(2): 99292
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i2/99292.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i2.99292