Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Feb 27, 2025; 17(2): 102328
Published online Feb 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i2.102328
Published online Feb 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i2.102328
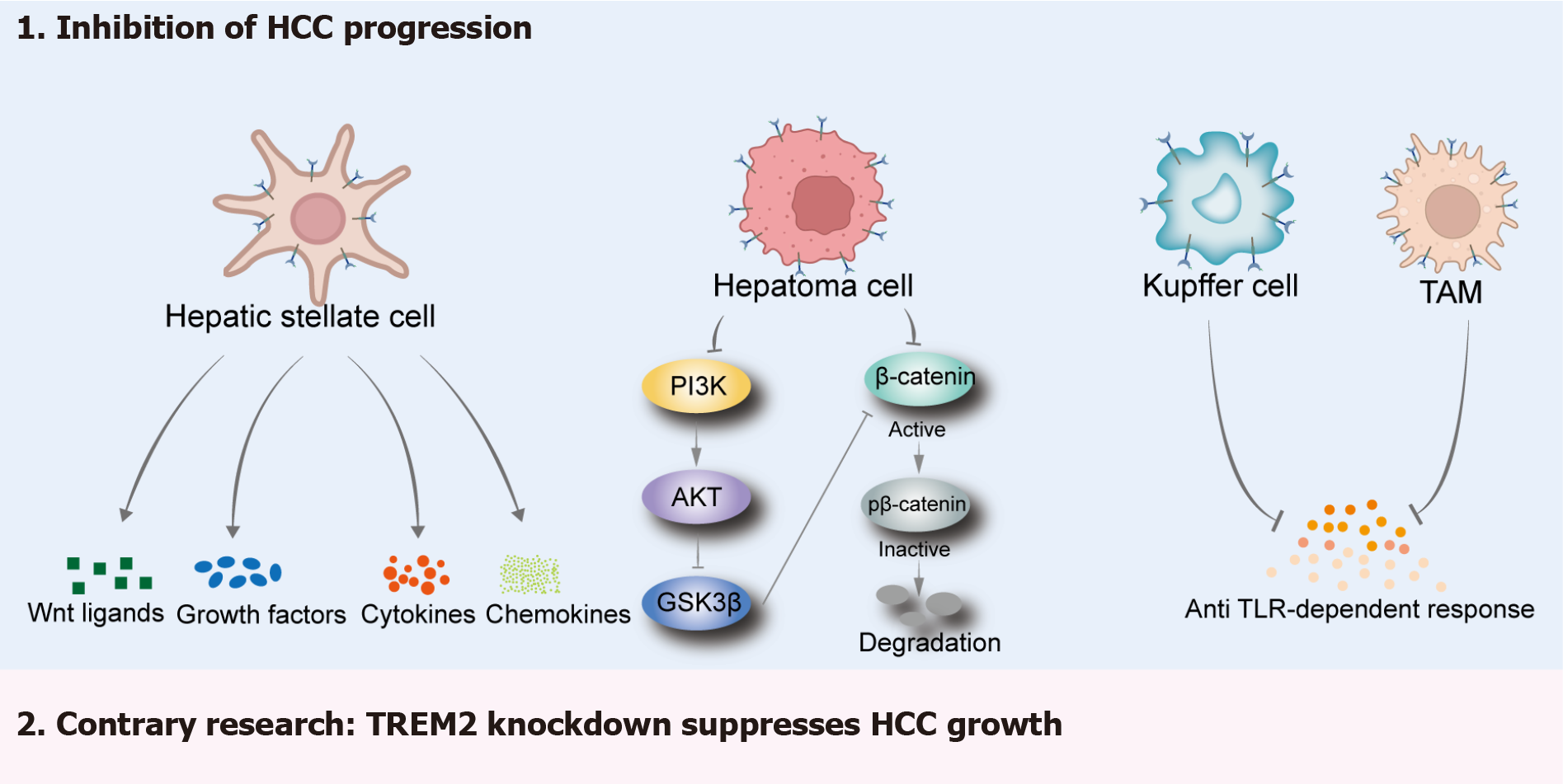
Figure 5 Bidirectional regulatory role of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 in Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-related hepatocellular carcinoma.
Overexpressed triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) in hepatic stellate cells can regulate the secretion of Wnt ligands and protect the liver from hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Overexpressed TREM2 in HCC cells can inhibit HCC progression by regulating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B/β-catenin pathway. During the development of end-stage HCC, TREM2 in Kupffer cells and tumor-associated macrophages may inhibit the occurrence of liver tumors by preventing toll like receptor-1 receptor-dependent responses. Another study revealed that TREM2 is a carcinogenic gene in the development of HCC. AKT: Protein kinase B; GSK3β: Glycogen synthase kinase-3β; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; TAMs: Tumor-associated macrophages; TLR: Toll like receptor; TREM2: Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2.
- Citation: Zhang LH, Liu ST, Zhao Q, Liu XY, Liu T, Zhang Q, Liu MH, Zhao WX. Role of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(2): 102328
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i2/102328.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i2.102328