Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Feb 27, 2025; 17(2): 101691
Published online Feb 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i2.101691
Published online Feb 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i2.101691
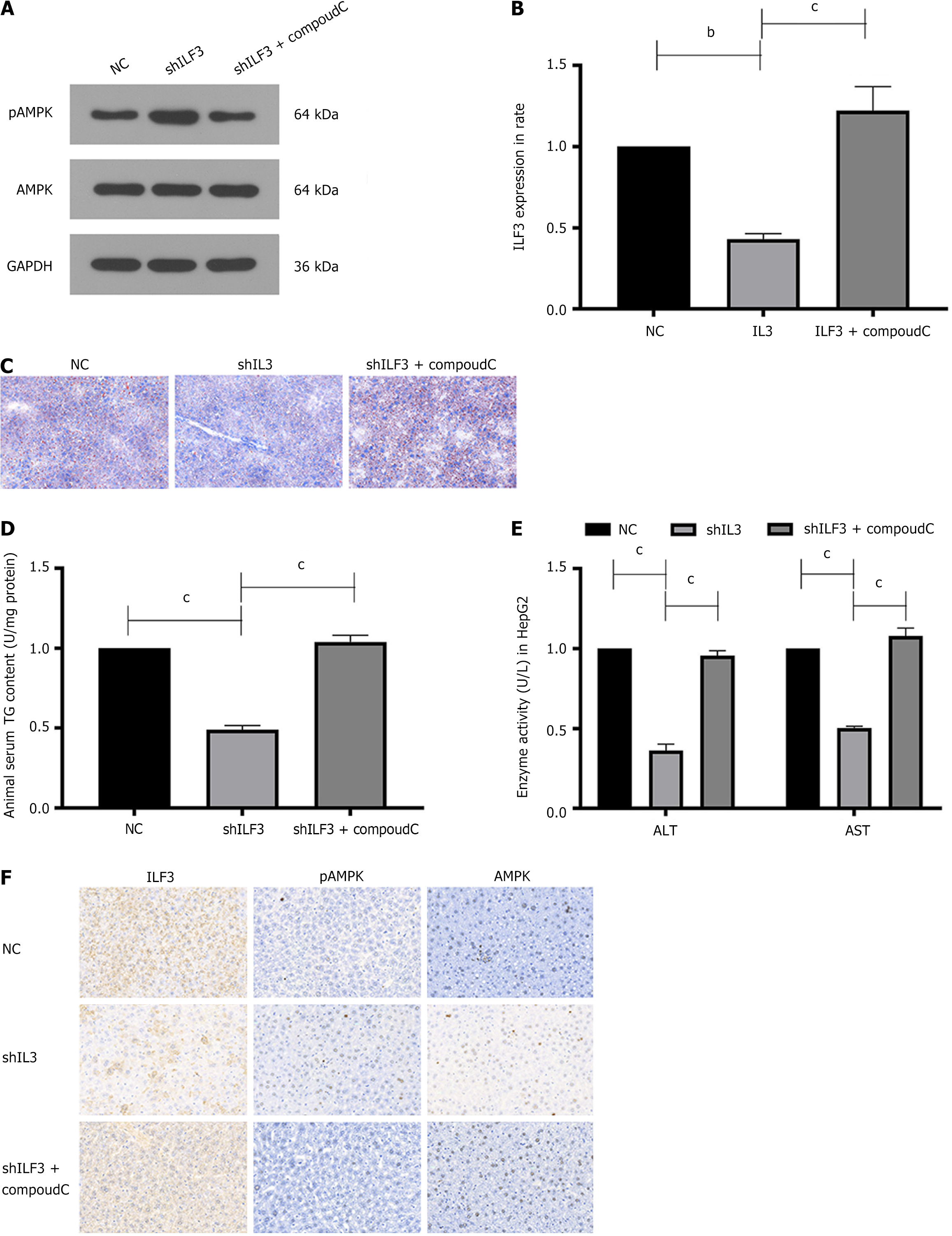
Figure 4 Knockdown of ILF3 alleviated non-alcoholic fatty liver disease progress by activating the AMPK pathway in vivo.
A and B: Western blotting showing knockdown of ILF3 helped activate the AMPK pathway in liver tissues; C: Oil Red O staining showed knockdown of ILF3 decreased lipid deposition in liver tissues, while CompoudC reversed this effect; D and E: Knockdown of ILF3 reduced triglyceride, alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase secretion in mice with high-fat diet feeding, while CompoudC reversed this effect; F: Knockdown of ILF3 was helpful to upregulate pAMPK expression, while CompoudC can reverse this effect. All data are presented as the mean ± SD. bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001; AST: Aspartate transaminase; ALT: Alanine transaminase; NC: Negative control; shILF3: Small hairpin RNA targeting LF3 intravenously.
- Citation: Zhan T, Liu JX, Huang M, Chen MT, Tian XR, Yang XL, Tan J, Zou YL, Han Z, Chen W, Tian X, Huang XD. ILF3 inhibits p-AMPK expression to drive non-alcoholic fatty liver disease progression. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(2): 101691
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i2/101691.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i2.101691