Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Jan 27, 2025; 17(1): 101664
Published online Jan 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i1.101664
Published online Jan 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i1.101664
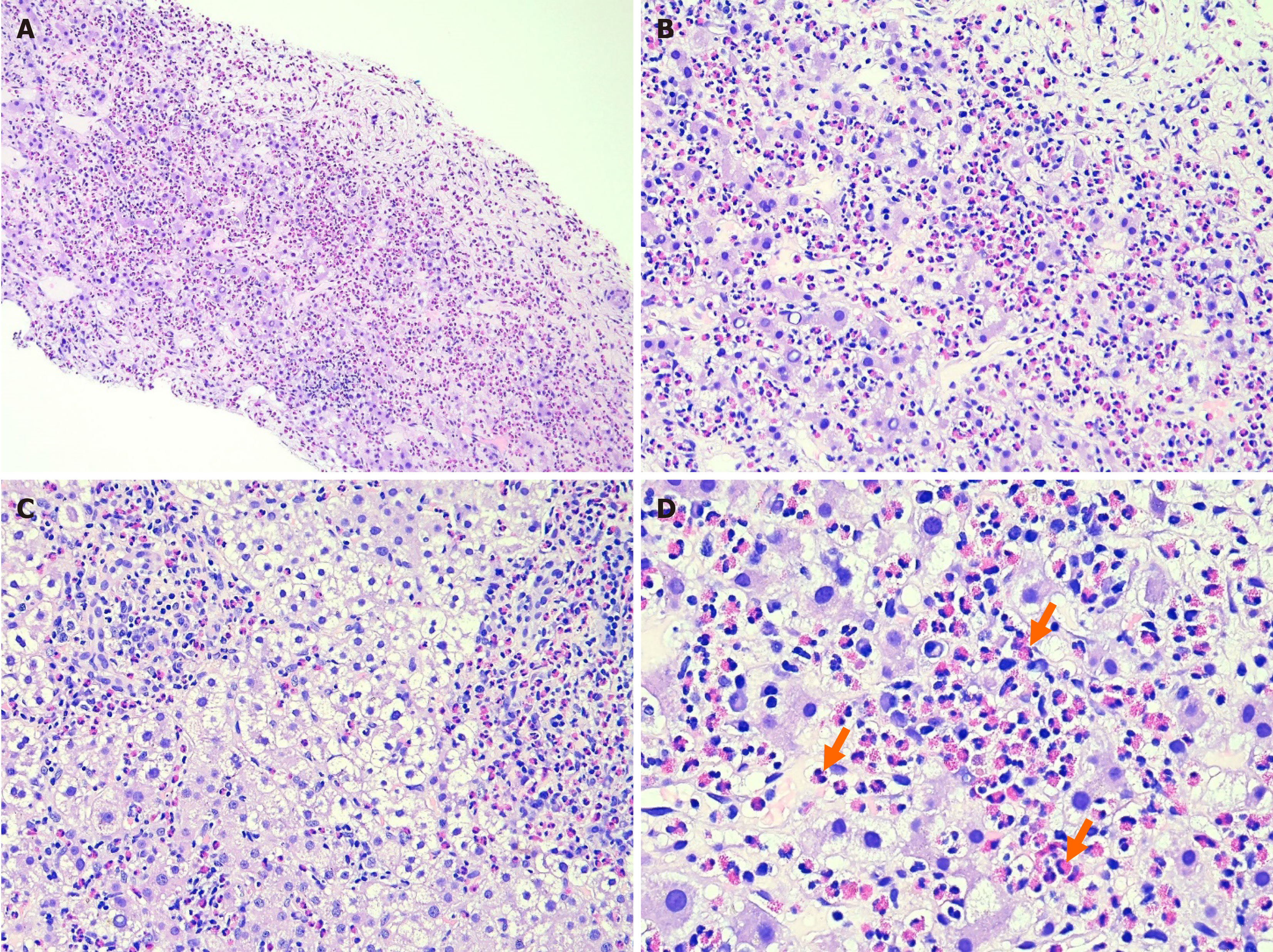
Figure 2 Marked eosinophil infiltration observed on a hematoxylin and eosin-stained liver biopsy specimen.
The biopsy showed dense infiltration of inflammatory cells, including lymphocytes and a significant number of eosinophils (orange arrows), in the periportal and lobular areas at various magnifications. A: 4 × magnification; B and C: 10 × magnification; D: 40 × magnification. No evidence of tumor tissue nor of malignant lesions was observed.
- Citation: Le KL, Tran MQ, Pham TN, Duong NNQ, Dinh TT, Le NK. Hepatic eosinophilic pseudotumor due to Fasciola hepatica infection mimicking intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A case report. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(1): 101664
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i1/101664.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i1.101664