Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Sep 27, 2024; 16(9): 1211-1228
Published online Sep 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i9.1211
Published online Sep 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i9.1211
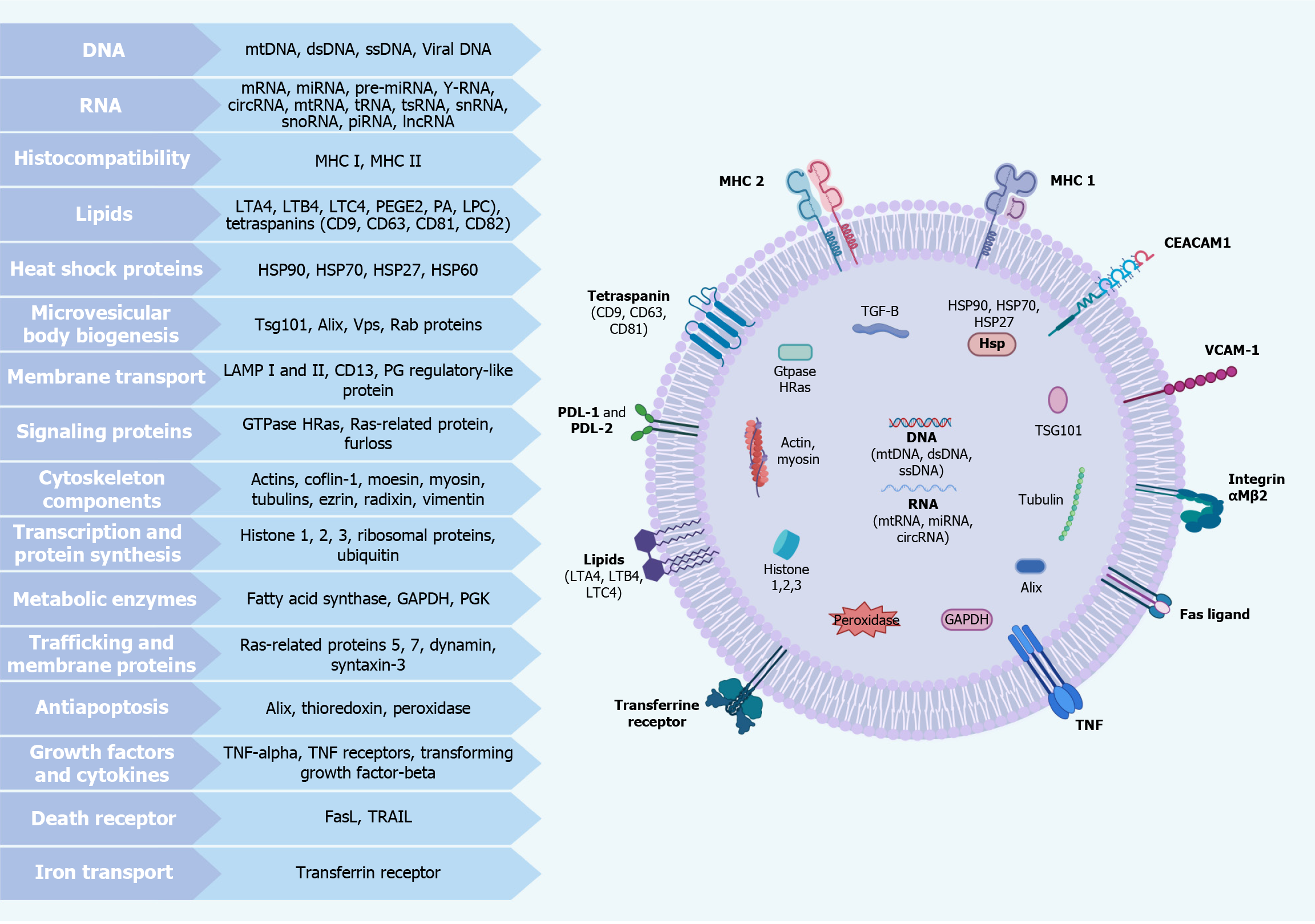
Figure 2 Exosomes: general molecular cargo.
This image shows exosome components and functions. Exosomes contain various nucleic acids [mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), single-stranded DNA (ssDNA), messenger RNA (mRNA), microRNA (miRNA), long non-coding RNA (lncRNA)], major histocompatibility complex I and II molecules, lipids [leukotriene A4 (LTA4), leukotriene D4 (LTD4), leukotriene C4 (LTC4), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), phosphatidic acid (PA), lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC)], and tetraspanins [(cluster of differentiation) CD9, CD63, CD81, CD82]. They also include heat shock proteins (HSP90, HSP70, HSP27, HSP60), multivesicular body proteins [tumor susceptibility gene 101 (TSG101), ALG-2 interacting protein X (Alix), vacuolar protein sorting-associated proteins (Vps), Rab proteins], membrane transport proteins [lysosome-associated membrane glycoproteins 1 and 2 (LAMP1 and LAMP2), CD13], signaling proteins (GTPase HRas), cytoskeleton components (actins, tubulins), transcription and synthesis elements (histones, ribosomal proteins), metabolic enzymes [GAPDH, phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK)], trafficking proteins (dynamin, syntaxin-3), anti-apoptosis proteins (ALIX), growth factors [tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-B)], death receptors [Fas ligand (FasL)], and iron transport proteins (transferrin receptor). Created in BioRender.com.
- Citation: Montoya-Buelna M, Ramirez-Lopez IG, San Juan-Garcia CA, Garcia-Regalado JJ, Millan-Sanchez MS, de la Cruz-Mosso U, Haramati J, Pereira-Suarez AL, Macias-Barragan J. Contribution of extracellular vesicles to steatosis-related liver disease and their therapeutic potential. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(9): 1211-1228
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i9/1211.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i9.1211