Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Sep 27, 2024; 16(9): 1211-1228
Published online Sep 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i9.1211
Published online Sep 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i9.1211
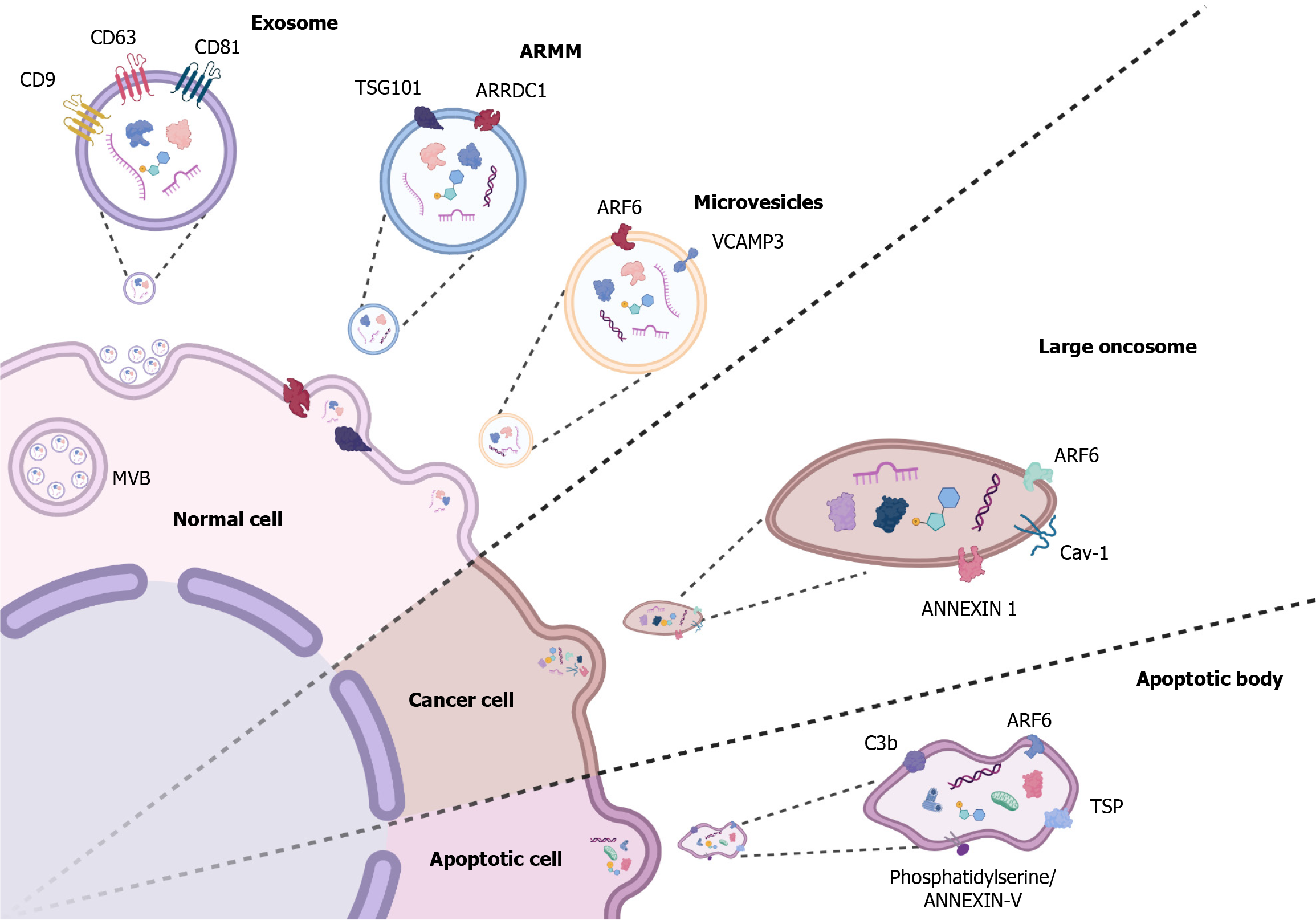
Figure 1 Extracellular vesicle biogenesis and molecular cargo.
The image shows the release of exosomes and microvesicles from normal, cancer, and apoptotic cells, including their associated molecules. Exosomes from normal cells contain cluster of differentiation (CD) 9, CD63, CD81, and tumor susceptibility gene 101 (TSG101). Arrestin domain-containing protein 1-mediated microvesicles (ARMM) feature arrestin domain containing 1 (ARRDC1). Microvesicles include ADP-ribosylation factor 6 (ARF6) and vesicle-associated membrane protein 3 (VCAMP3). Large oncosomes from cancer cells contain ARF6, Caveolin-1 (Cav-1), and ANNEXIN 1. Apoptotic bodies from apoptotic cells include ARF6, complement component 3b (C3b), thrombospondin (TSP), and phosphatidylserine/ANNEXIN-V. These extracellular vesicles play critical roles in intercellular communication, carrying proteins and nucleic acids that influence recipient cell behavior. MVB: Multivesicular body. Created in BioRender.com.
- Citation: Montoya-Buelna M, Ramirez-Lopez IG, San Juan-Garcia CA, Garcia-Regalado JJ, Millan-Sanchez MS, de la Cruz-Mosso U, Haramati J, Pereira-Suarez AL, Macias-Barragan J. Contribution of extracellular vesicles to steatosis-related liver disease and their therapeutic potential. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(9): 1211-1228
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i9/1211.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i9.1211