Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Jul 27, 2024; 16(7): 1051-1066
Published online Jul 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i7.1051
Published online Jul 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i7.1051
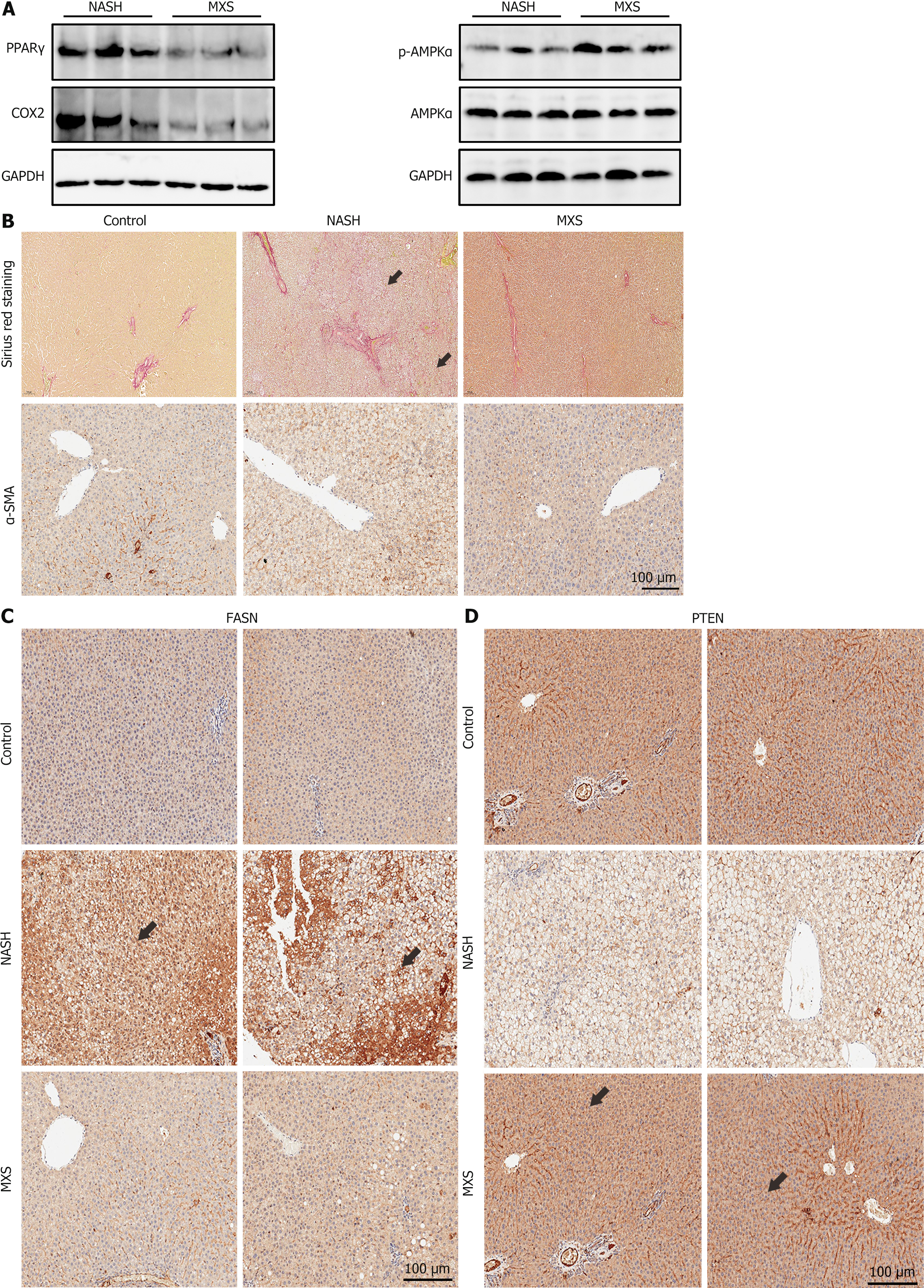
Figure 8 Modified Xiaoyao San treatment regulated the signaling pathways and factors related to inflammation and lipid metabolism.
A: In hepatic tissues, PPARγ and COX2 expressions were decreased by modified Xiaoyao San (MXS) treatment and MXS also activated the AMPK signaling; B: MXS treatment attenuated hepatic fibrosis and α-SMA expression. Collagen fibers appear red (black arrows) under normal light microscopy and other tissue components were dyed yellow; C: The MXS treatment inhibited the levels of FASN in liver tissues; D: The PTEN expression in liver tissues was restored after MXS treatment (immunohistochemistry detection reagents yielding a brown reaction product, indicated by black arrows). The brown portion is the portion of the antigen that expresses coloration. MXS: Modified Xiaoyao San; NASH: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
- Citation: Mei XL, Wu SY, Wu SL, Luo XL, Huang SX, Liu R, Qiang Z. Hepatoprotective effects of Xiaoyao San formula on hepatic steatosis and inflammation via regulating the sex hormones metabolism. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(7): 1051-1066
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i7/1051.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i7.1051