Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Jul 27, 2024; 16(7): 1051-1066
Published online Jul 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i7.1051
Published online Jul 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i7.1051
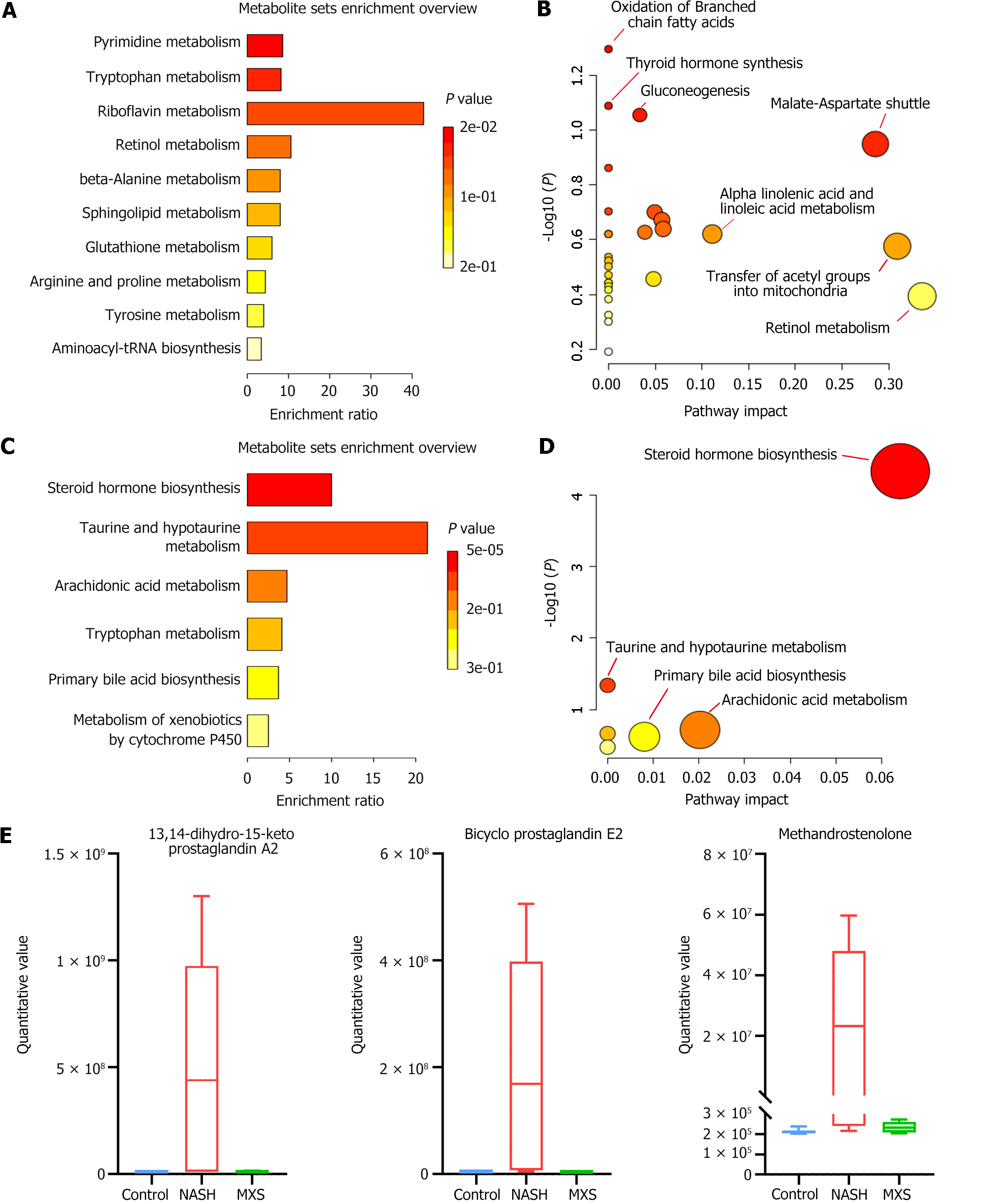
Figure 6 Modified Xiaoyao San inhibited steroid synthesis and inflammation-related metabolic pathways.
A and B: Metabolite set enrichment and pathway analysis of the 30 identified metabolites that decreased in the nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) model group but recovered or increased after modified Xiaoyao San (MXS) treatment; C and D: Metabolite set enrichment and pathway analysis of the 30 identified metabolites that unusually increased in the NASH model group but recovered or were downregulated after MXS treatment; E: Histogram of the top 3 metabolites related to steroid hormones and the inflammation process. MXS: Modified Xiaoyao San; NASH: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
- Citation: Mei XL, Wu SY, Wu SL, Luo XL, Huang SX, Liu R, Qiang Z. Hepatoprotective effects of Xiaoyao San formula on hepatic steatosis and inflammation via regulating the sex hormones metabolism. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(7): 1051-1066
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i7/1051.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i7.1051