Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Jul 27, 2024; 16(7): 1051-1066
Published online Jul 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i7.1051
Published online Jul 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i7.1051
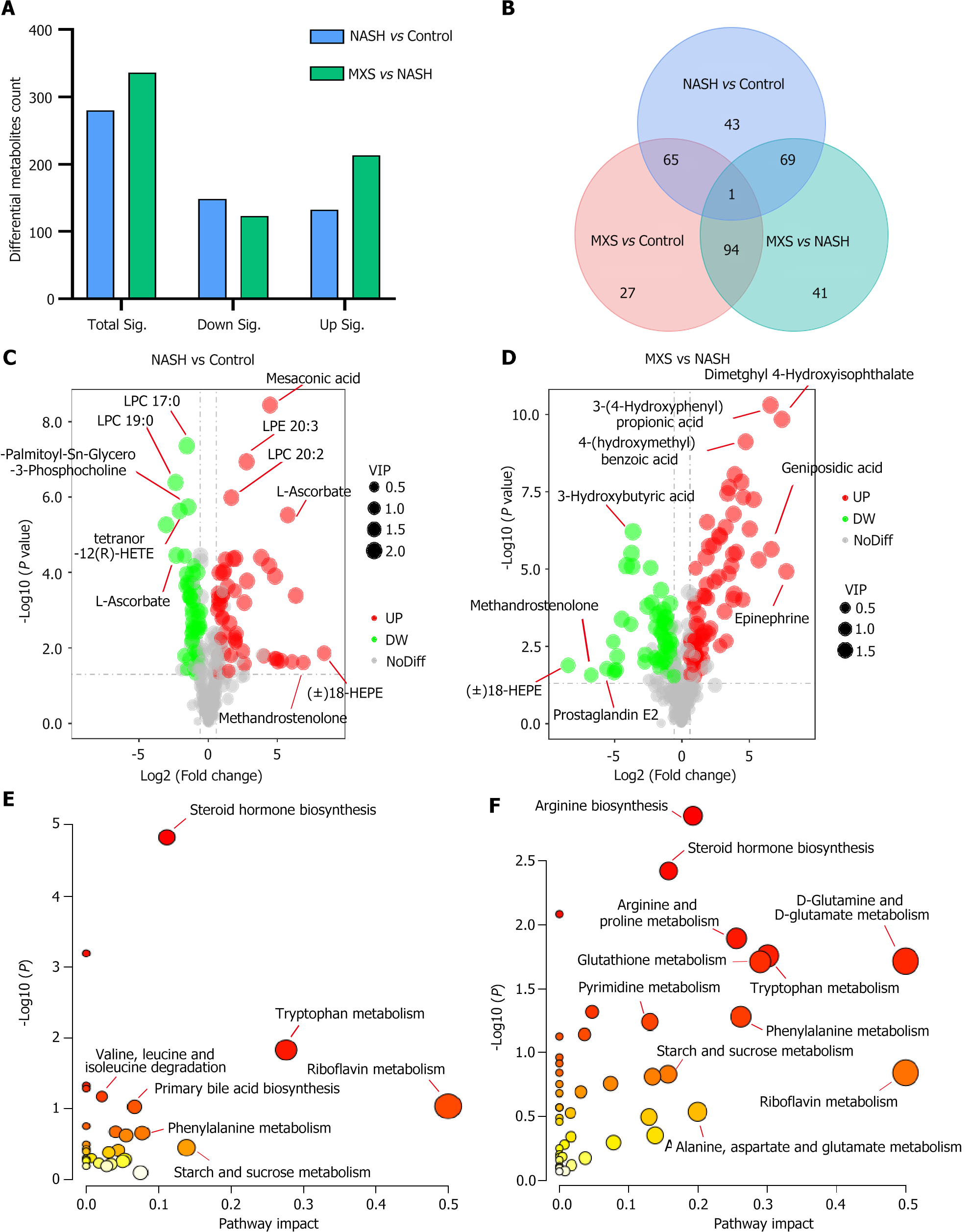
Figure 3 Steroid hormone synthesis was the primary target pathway affected by modified Xiaoyao San treatment.
A: Statistical analysis of differential metabolites. Total Sig denoted the total count of metabolites that exhibited significant changes. Down/up Sig represented the overall number of metabolites that underwent significant downregulation or upregulation; B: A Venn diagram illustrated the comparative analysis of metabolites among the three groups; C and D: Volcano plots displayed significantly changed metabolites, indicated by red and blue-colored dots. The criteria for significance were fold change (FC) below than 0.667, FC greater than 1.5, or variable importance in the projection greater than 1.0, and P value below than 0.05; E and F: Pathway enrichment analysis of differential metabolites in different comparisons. The pathway impact value (X-axis) was denoted by the size of the circles, and the -log10 P value weight (ranging from white to red, Y-axis) was indicated by the color intensity. MXS: Modified Xiaoyao San; NASH: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
- Citation: Mei XL, Wu SY, Wu SL, Luo XL, Huang SX, Liu R, Qiang Z. Hepatoprotective effects of Xiaoyao San formula on hepatic steatosis and inflammation via regulating the sex hormones metabolism. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(7): 1051-1066
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i7/1051.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i7.1051