Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Jul 27, 2024; 16(7): 1051-1066
Published online Jul 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i7.1051
Published online Jul 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i7.1051
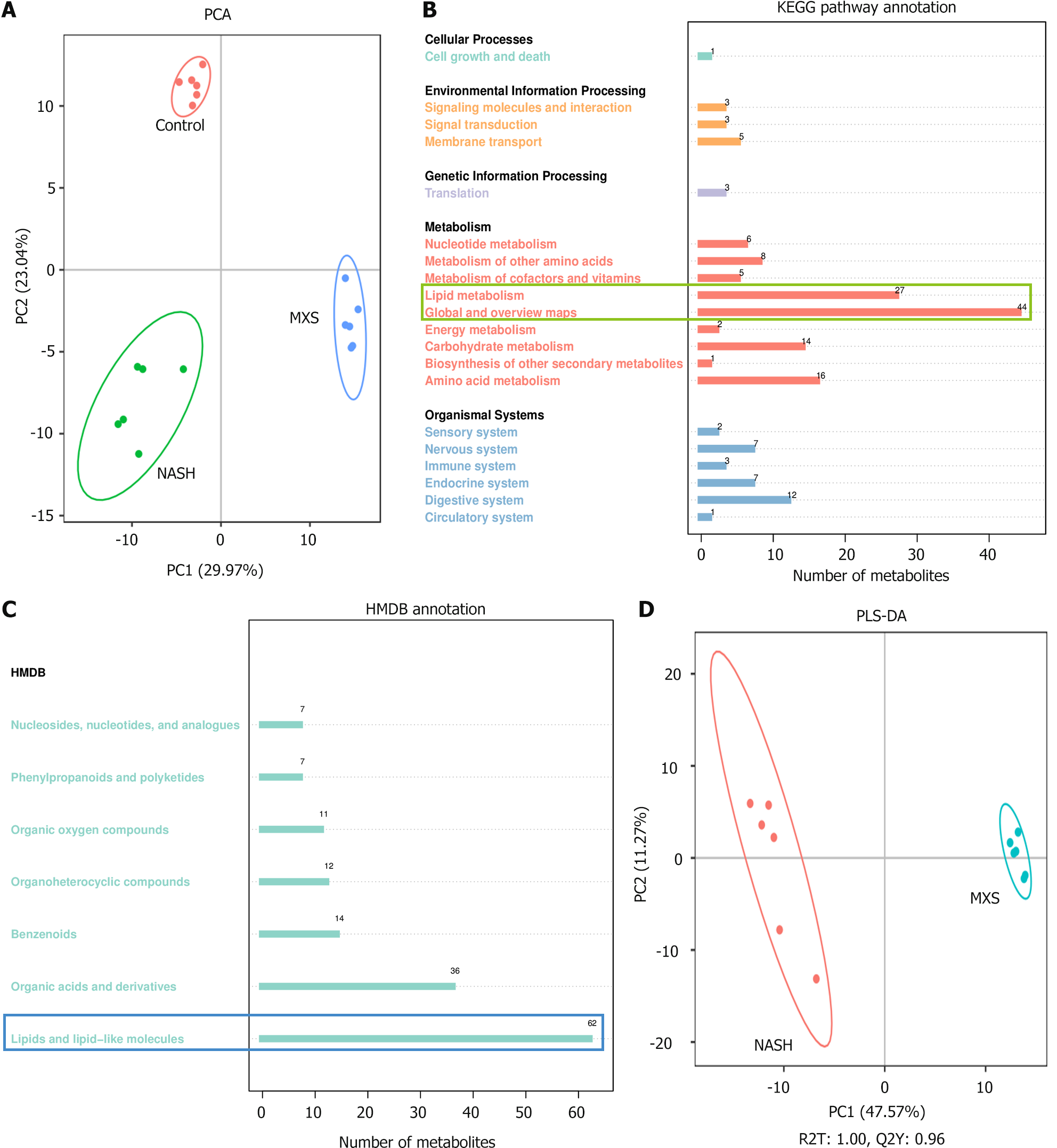
Figure 2 Significant changes in metabolites after modified Xiaoyao San treatment were mainly related to lipid metabolism.
A: Principal component analysis score map of each group; B: Gene ontology enrichment analyses; C: Human Metabolome Database classification notes; D: Partial least squares discrimination analysis between nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and modified Xiaoyao San groups. The scores of the first-ranked principal component (PC1, horizontal) and the second-ranked principal component (PC2, vertical) were used to represent the data. Samples from various experimental cohorts were represented by differently colored scatter plots, while 95% confidence intervals were visually depicted using ellipses. PCA: Principal component analysis; PLS-DA: Partial least squares discrimination analysis; HMDB: Human Metabolome Database; MXS: Modified Xiaoyao San; NASH: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
- Citation: Mei XL, Wu SY, Wu SL, Luo XL, Huang SX, Liu R, Qiang Z. Hepatoprotective effects of Xiaoyao San formula on hepatic steatosis and inflammation via regulating the sex hormones metabolism. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(7): 1051-1066
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i7/1051.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i7.1051