Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Jul 27, 2024; 16(7): 1051-1066
Published online Jul 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i7.1051
Published online Jul 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i7.1051
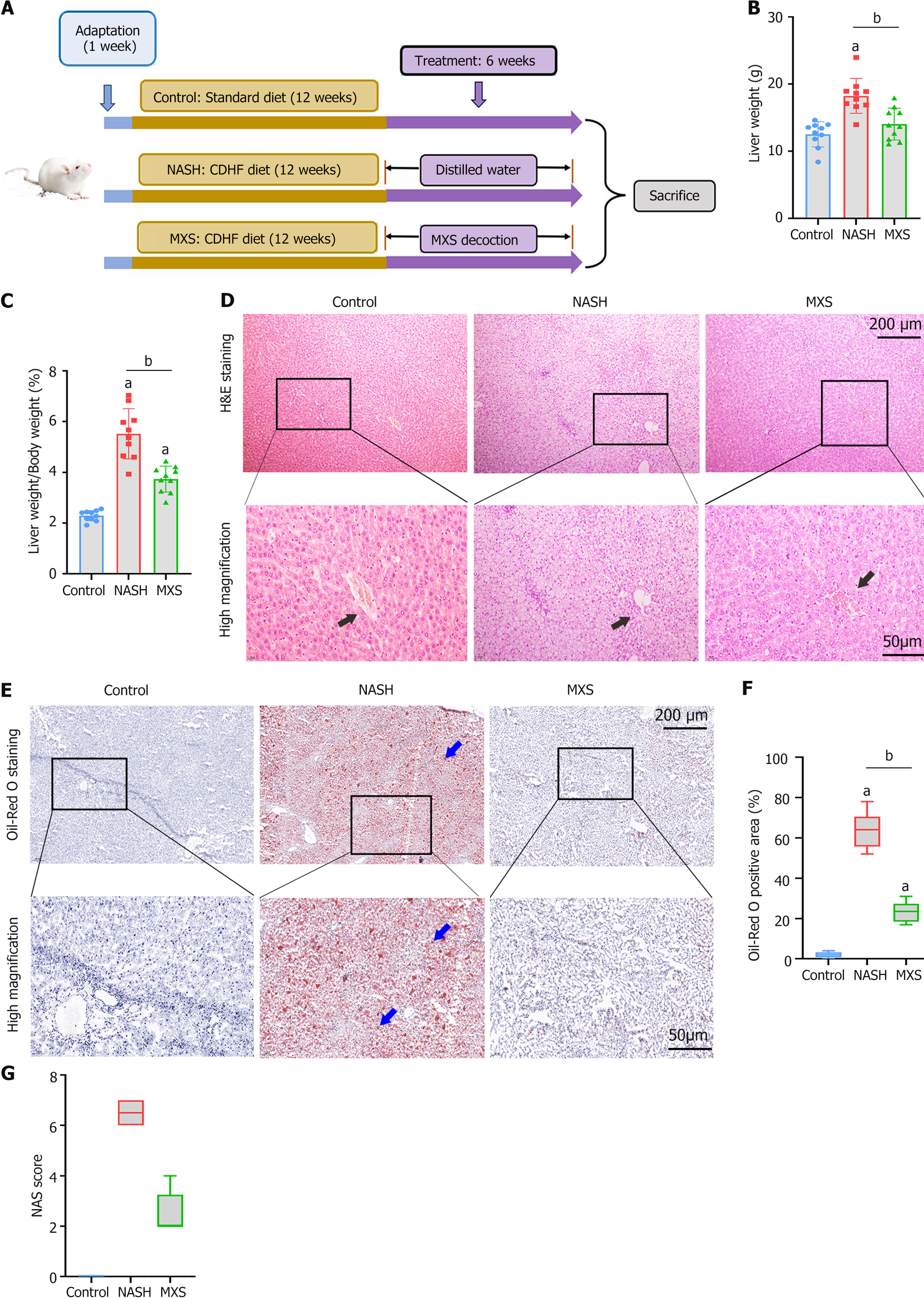
Figure 1 Modified Xiaoyao San demonstrated its capacity to alleviate inflammation and hepatic steatosis in rats subjected to a choline-deficient/high-fat diet.
A: The diagram illustrating the experimental procedure outlined the systematic investigation of the protective role of modified Xiaoyao San (MXS) in rats following a 12-week choline-deficient/high-fat (CDHF) diet regimen. Starting at week 13, rats that had been fed the CDHF diet received daily intragastric administration of either saline or MXS decoction for a duration of 6 weeks; B and C: The liver weight and liver/body weight ratio of the rat groups were presented; D and E: The images from hepatic sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin and Oil Red O (ORO). Black arrows indicate the liver portal areas. The lipid droplets (indicated by blue arrows) in the tissue are orange-red and the nuclei are blue; F and G: Quantitative data pertaining to ORO-positive areas and the nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity score for each group were displayed. Data were presented as mean ± standard error of mean (n = 10/group), and were analyzed by ANOVA. aP < 0.05 Control vs nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) group. bP < 0.05 NASH vs MXS group. MXS: Modified Xiaoyao San; NASH: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
- Citation: Mei XL, Wu SY, Wu SL, Luo XL, Huang SX, Liu R, Qiang Z. Hepatoprotective effects of Xiaoyao San formula on hepatic steatosis and inflammation via regulating the sex hormones metabolism. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(7): 1051-1066
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i7/1051.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i7.1051