Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Jun 27, 2024; 16(6): 932-950
Published online Jun 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i6.932
Published online Jun 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i6.932
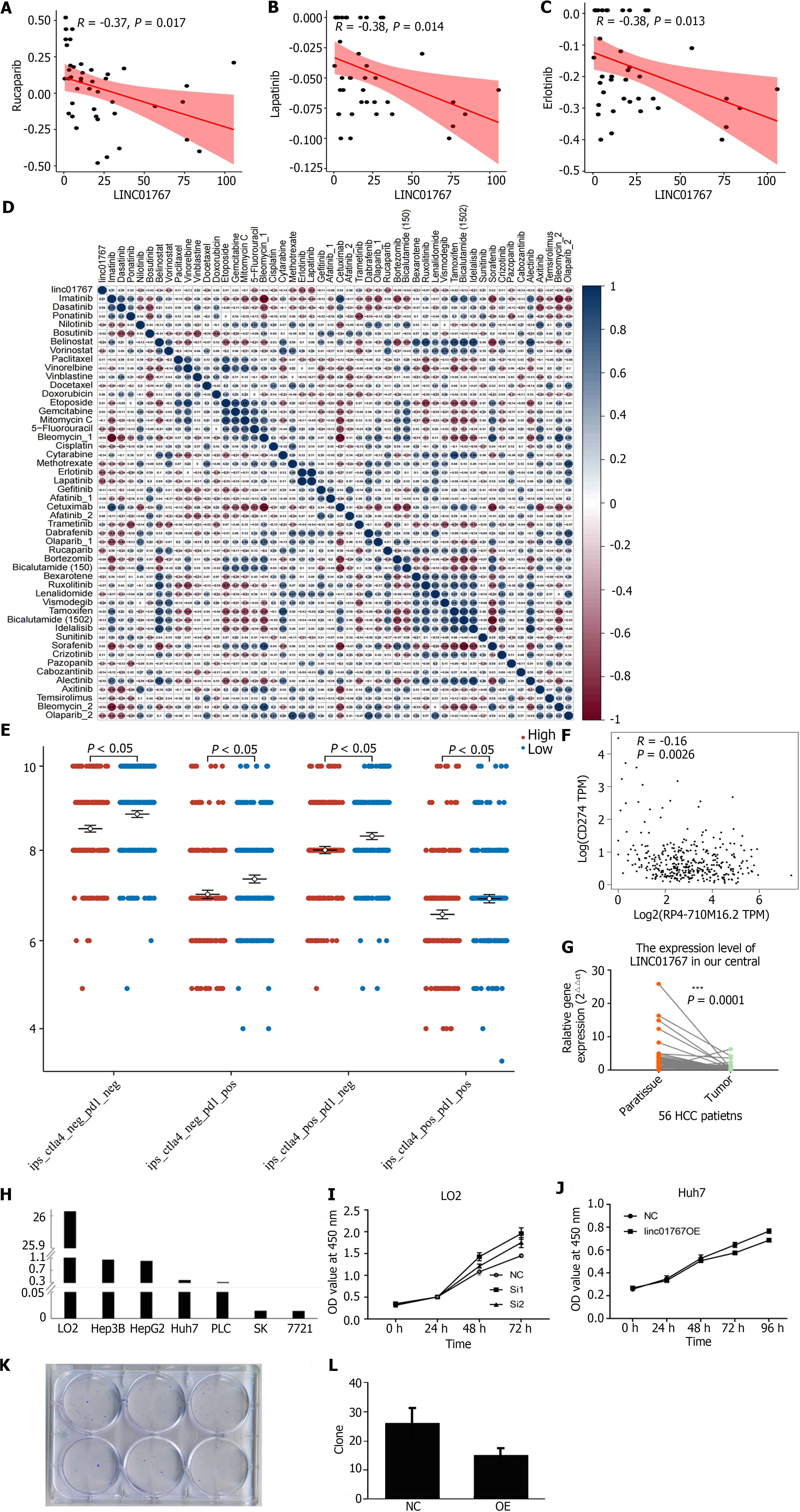
Figure 4 The role of LINC01767 of predicting drug sensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma and the invitro experiment to valid the role of LINC01767 in Huh7.
A: The re-analysis results of the previous research showed LINC01767 was negatively with the sensitivity of rucapanib (R = -0.37, P = 0.017); B: Lapatinib (R = -0.38, P = 0.014); C: Erlotinib (R = -0.38, P = 0.013); D: Sperman correlation analysis was used to evaluate the mRNA level of LINC01767 and IC50 of the potential drugs; E: The immunophenoscore (IPS), IPS-programmed cell death protein 1 (PD1)/programmed cell death ligand 1 (PDL1)/PD-L2 and IPS-CTLA4 were significantly lower higher in different between LINC01767 high group than in low groups (all P < 0.05); F: The spearman correlation analysis showed LINC01767 was negatively correlated with PDL1, P = 0.0026; G: The quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction of tumor tissue and para-tumor tissue from hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients in our cohort showed that the LINC01767 was down regulated obviously in tumor; H: The cell lines of HCC and normal cell LO2 showed that the LINC01767 was down regulated in cancer cell line comparing with LO2; I: The down regulation of LINC01767 in LO2 cell showed the growth of the LO2 was impeded; J: MTT method and formation of clones was conducted to observe cell proliferation showing the overexpression of LINC01767 inhibit the cell proliferation; K and L: LINC01767 over expression impede the clone formation of Huh7. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; NC: Normal control; OE: Over expression.
- Citation: Zhang L, Cui TX, Li XZ, Liu C, Wang WQ. Diagnostic and prognostic role of LINC01767 in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(6): 932-950
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i6/932.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i6.932